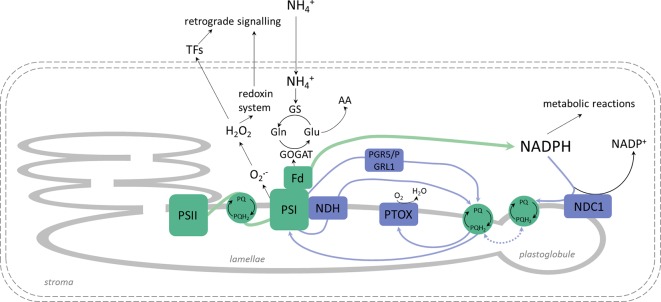
Figure 10.
Changes in chlETC functioning, linear electron transport (LET; green arrows) route and alternative electron pathways (blue arrows) under nutrition. The inevitable activity of the glutamine synthetase - glutamine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase (GS-GOGAT) cycle consumes electrons from ferredoxin (Fd) for assimilation into amino acids (AA). Higher NAD(P)H dehydrogenase C1 (NDC1) protein abundance in plastoglobules transfers electrons from NADPH to plastoquinone (PQ), balancing the stromal redox pool. Consequently, less free PQ are available for cyclic electron transport (CET), and the PQ pool is more reduced in grana lamellae. Electrons from photosystem I (PSI) enter pseudocyclic electron transport (water-to-water cycle), which may lead to reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in chloroplasts. H2O2 may be engaged in signaling, and plastid terminal oxidase (PTOX) may act as the positive regulator of chloroplast to nucleolus retrograde signaling or communication with the alternative oxidase (AOX).