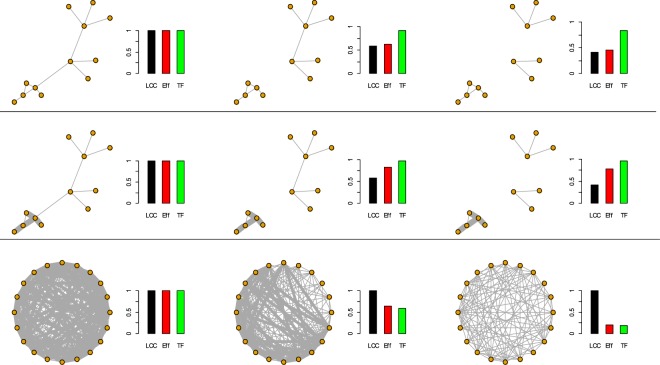
Figure 1.
The network functioning measures. Simple examples of model networks under link removal depicting the different interpretation of the system functioning furnished by the measures used in this paper. The bar plot at the right of each network indicates the value of the functioning measures (normalized on the initial network functioning value). The links width indicates the link weights. Top row: topological (binary) sparse network; half row: weighted sparse network; bottom row: fully connected weighted network. The LCC quickly collapses in the sparse topological (binary) network with two link removals; Eff follows the LCC decrease whereas the TF holds almost unaltered (Fig. 1 top row). Introducing heterogeneity in link weights over the same sparse network, now the Eff does not follow the LCC decrease acting more similar to the TF (Fig. 1 half row). In the last row we depict a fully connected weighted network under higher weight link removals (strong links) the LCC holds constant under strong links pruning where instead Eff and TF quickly decrease (Fig. 1 bottom row).