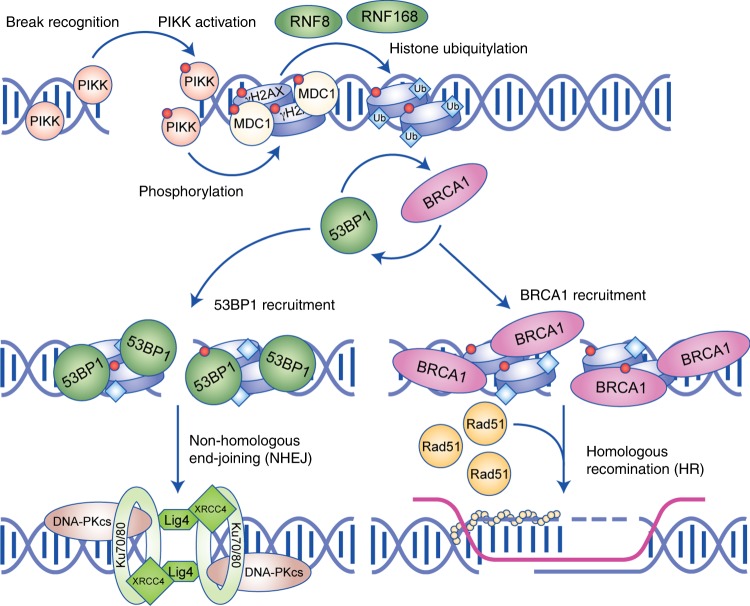
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of the double-stranded break (DSB) repair cascade. Initial recognition of the break recruits the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-like kinases (PIKKs), resulting in its activation by autophosphorylation. Activated PIKKs then phosphorylates early participants of the cascade, H2AX and MDC1. The ubiquitin ligase RNF8 recognises and is recruited to phosphorylated MDC1 at the break site, initiating the ubiquitylation of histone H1, which subsequently recruits RNF168 to ubiquitylate H2A. The modified chromatin acts as a marker for the competitive recruitment of either 53BP1 or BRCA1, which facilitate either non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) or homologous recombination (HR), respectively. NHEJ repair is dependent on the recruitment of the DNA–PK complex (Ku70–80 bound to DNA–PKcs) and end-processing factors such as XRCC4 and Lig4. HR is dependent on resection of the broken DNA to produce a single-stranded DNA overhang that gets coated in a RAD51 filament and invades the sister-chromatid to facilitate templated repair.