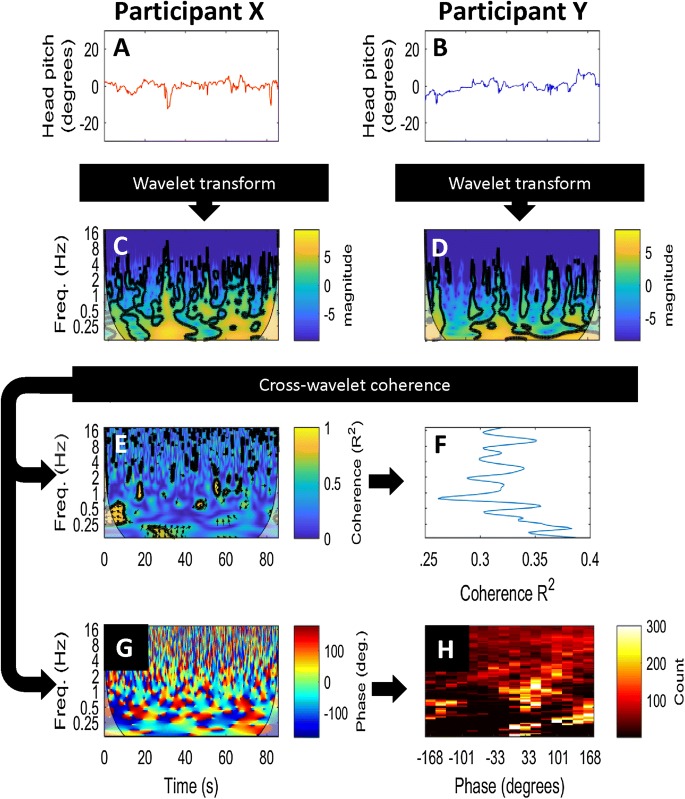
Fig. 2.
Data analysis methods. For each trial of true interaction, the head motion traces for the two participants (a, b) were subject to a wavelet transformation giving c and d. The cross-wavelet coherence was calculated to give coherence (e) and phase angle (g) across the frequency spectrum for all time points during the trial. The coherence (e) was averaged over time (f) and then over all dyads to obtain the average coherence across the frequency spectrum in real interactions. The phase angles (g) were binned by angle and frequency (collapsing over time) (h) and then averaged over all dyads. To calculate coherence and phase angle in pseudo-interactions, the same procedure was used with mismatched data replacing the inputs a and b