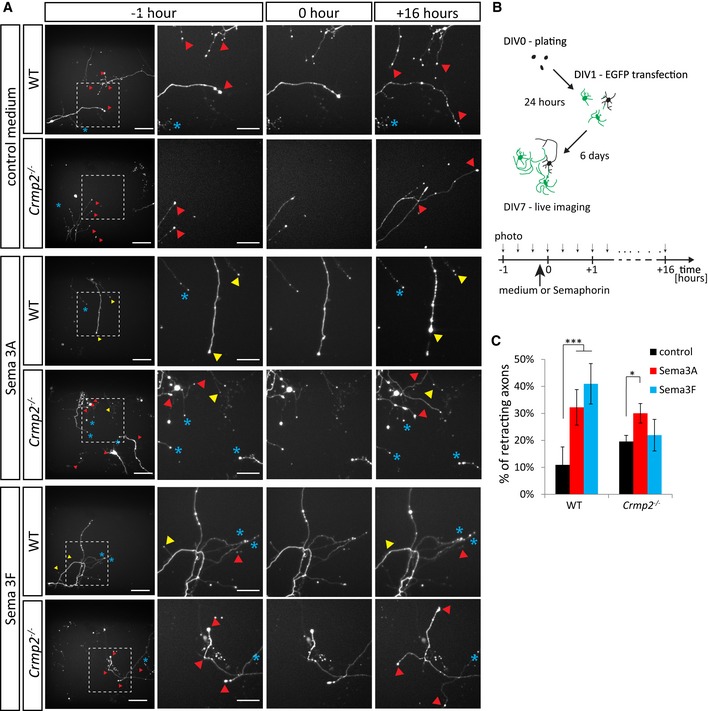
Time‐lapse imaging of DIV7 cultured hippocampal neurons before and after semaphorin stimulation. Upper panel: axon growth without semaphorin stimulation. Middle panel: stimulation with Sema3A (0 h) (1 nM,
n = 669 axons for WT, 761 axons for knockout) causes retraction of both WT and
crmp2
−/− neurons. Lower panel: stimulation with Sema3F (5 nM,
n = 602 axons for WT, 955 axons for knockout) causes axon retraction in WT, but not in
crmp2
−/− neurons. Red triangles depict growing axons, yellow retracting axons, and blue asterisks indicate steady non‐growing axons. See also
[Link],
[Link]. Scale bars: 100 μm (whole image field) and 50 μm (magnified).