Figure 6. The schematic diagram showing the mechanisms of Tau‐induced anti‐apoptosis.
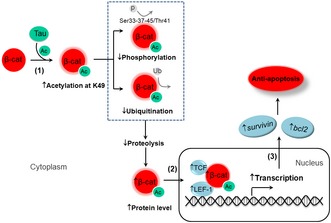
(1) Tau acetylates β‐catenin at K49, which inhibits K49 ubiquitination, Ser45/Thr41/Ser37/Ser33 phosphorylation and proteolysis of β‐catenin, leading to β‐catenin upregulation. (2 and 3) The increased β‐catenin is translocated into the nuclei (2) where it promotes transcription activity and increases expression of bcl2 and survivin leading to cellular anti‐apoptosis (3).
