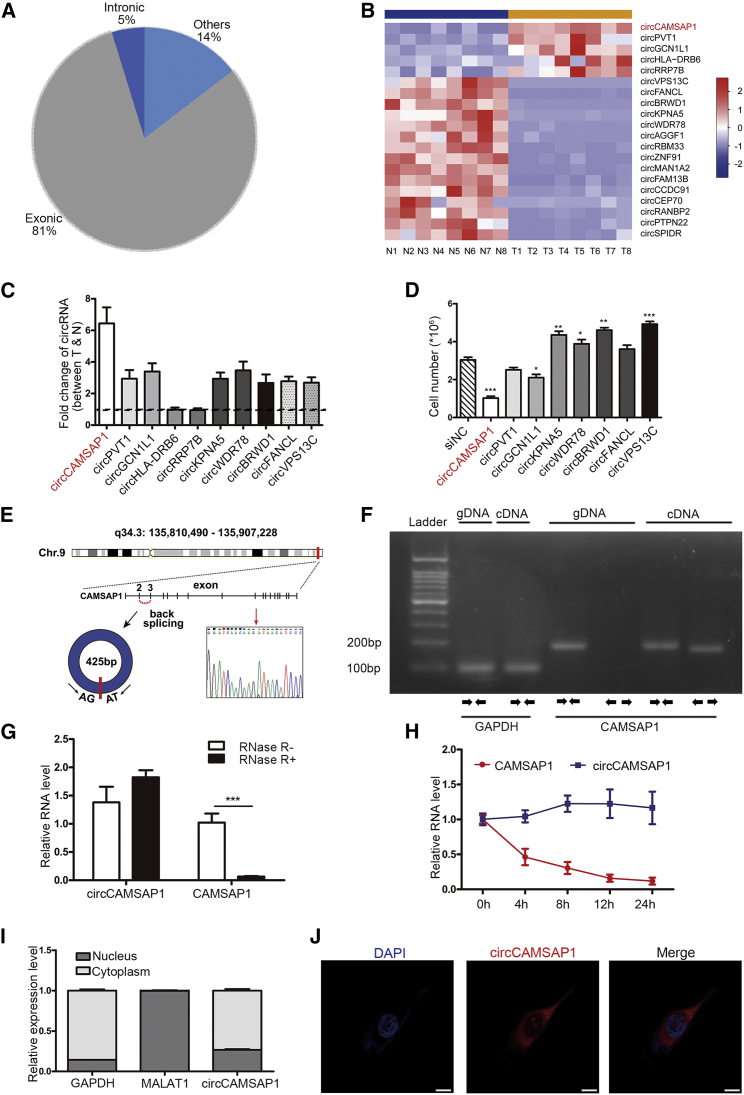
Figure 1.
circRNA Expression Profile in CRC and Characterization of circCAMSAP1
(A) Genomic origin of circRNAs (n = 31,557) identified in human CRC tissues. 25,458 were derived from exons, 1,505 were derived from introns, and 4,594 were derived from the others. (B) Heatmap of the differentially expressed circRNAs in eight pairs of human CRC tissues and the matched non-tumor tissues. (C) Fold change of 10 indicated circRNAs expression between 20 CRC tumor tissues and adjacent non-tumor tissues validated by qPCR. N, non-tumor tissues; T, tumor tissues. (D) HCT15 cell numbers in indicated siRNA-treated groups compared to negative control (NC) control group on fifth day after siRNA treatment. (E) Genomic loci of the CAMSAP1 gene and circCAMSAP1. Red arrow indicates the back-splicing of CAMSAP1 exon 2 to exon 3 confirmed by Sanger sequencing. (F) RT-PCR for the analysis of the existence of circCAMSAP1 using the divergent primers and convergent primers in HCT15 cells. GAPDH was used as a control for a linear RNA transcript. (G) qRT-PCR analysis of circCAMSAP1 and CAMSAP1 linear mRNA with or without RNase R treatment. (H) qRT-PCR analysis of the abundance of circCAMSAP1 and CAMSAP1 linear mRNA in HCT15 cells treated with actinomycin D at the indicated time points. (I) Results of cytoplasmic and nuclear mRNA fractionation experiment. GADPH served as a marker of cytoplasmic location, while MALAT1 served as a marker of nuclear location. (J) Representative images for FISH circCAMSAP1 staining in HCT15 cells. The circCAMSAP1 probe was labeled with Cy3 (red); nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 5 μm. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 by Student’s t test. Error bars indicate SD.