Figure 2. Equilibrium and free energy calculations for protein–lipid interactions.
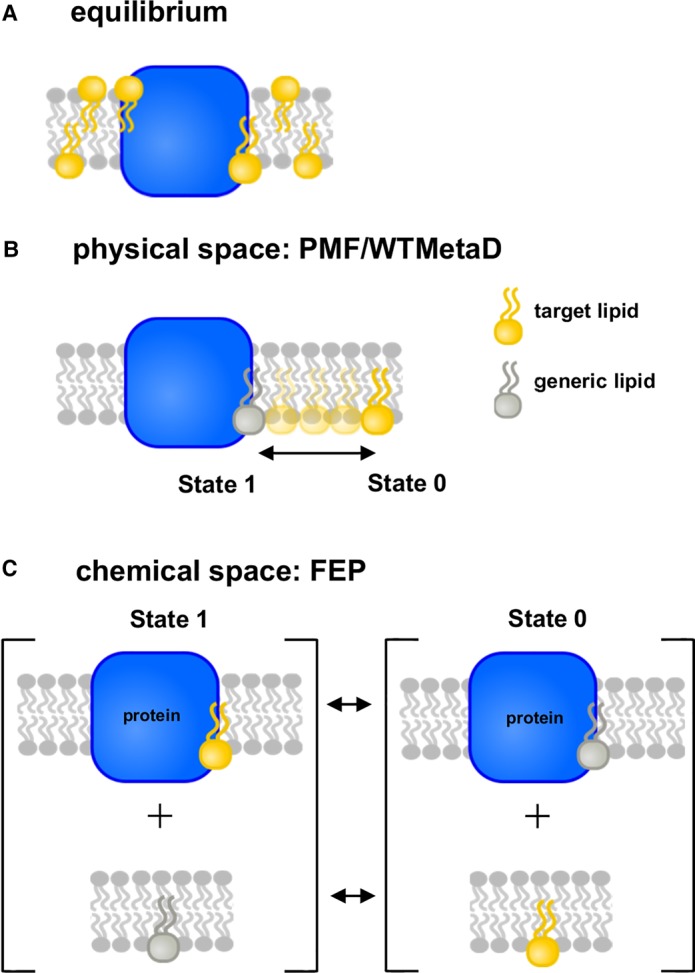
(A) Equilibrium simulations allow multiple protein–lipid events to occur in an unbiased fashion over long MD simulations. (B) Construction of a reaction co-ordinate in physical space requires sampling of the protein–lipid complex (State 1) and of the lipid free in membrane (State 0) as well as many intermediate positions of the lipid between the binding site and surrounding bilayer bulk. Note that in State 0, the lipid binding site on the protein will be occupied by a generic lipid. (C) Sampling States 1 and 0 in chemical space. This is done over two sets of simulations: first, whilst bound to the protein, the target lipid (yellow) is alchemically transformed into a background (generic e.g. PC; grey) lipid (upper panels). At the same time, a background lipid free in the bilayer is also transformed in a target lipid molecule. Combining the upper and lower calculations yields the free energy for binding of the target lipid relative to that of a background lipid.
