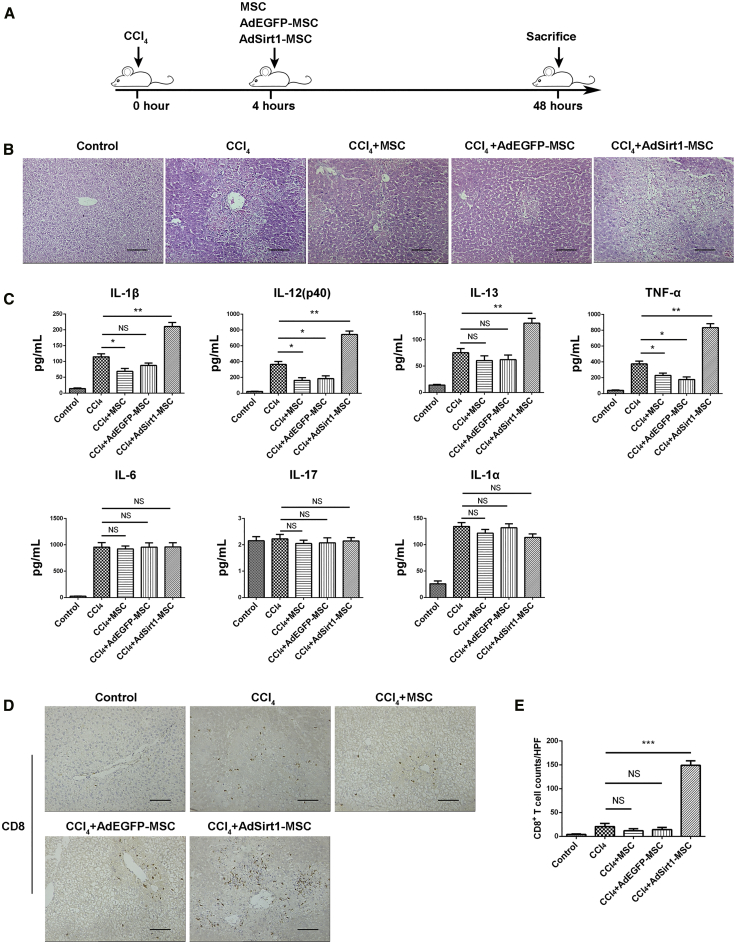
Figure 2.
The Administration of AdSirt1-MSCs Promotes Liver Inflammation in Mice with CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Injury
(A) Schematic diagram depicting the experimental approach to evaluate the effect of the AdSirt1-MSC transfusion on mice with acute liver injury induced by CCl4. The mice were randomly divided into five experimental groups as described in Materials and Methods. (B) H&E-stained sections of liver tissues from the animals of the above five groups (48 h post-treatment). Representative images are shown for each sample. Scale bars, 100 μm. (C) Pro-inflammatory cytokine production of IL-1β, IL-12(p40), IL-13, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-17, and IL-1α was detected in serum of mice from the above five animal groups (48 h post-treatment) by Bio-Plex analysis. **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 versus CCl4 group. p > 0.05 versus CCl4 group; NS, not significant (p > 0.05). (D) Representative samples of immunochemistry staining of CD8+ T cells in liver tissue of mice from the above five groups (48 h post-treatment). The black arrows indicate CD8+ T cells. (E) Quantification of the CD8+ T cell populations identified by CD8 immunostaining in liver sections of mice from the above five animal groups (48 h post-treatment). Scale bars, 100 μm. The counts of CD8+ T cells were measured by counting five randomly selected ×200 high-power fields (HPFs) per paraffin section under light microscopy. Scale bars, 100 μm. ***p < 0.001 versus CCl4 group. p > 0.05 versus CCl4 group; NS, not significant (p > 0.05).