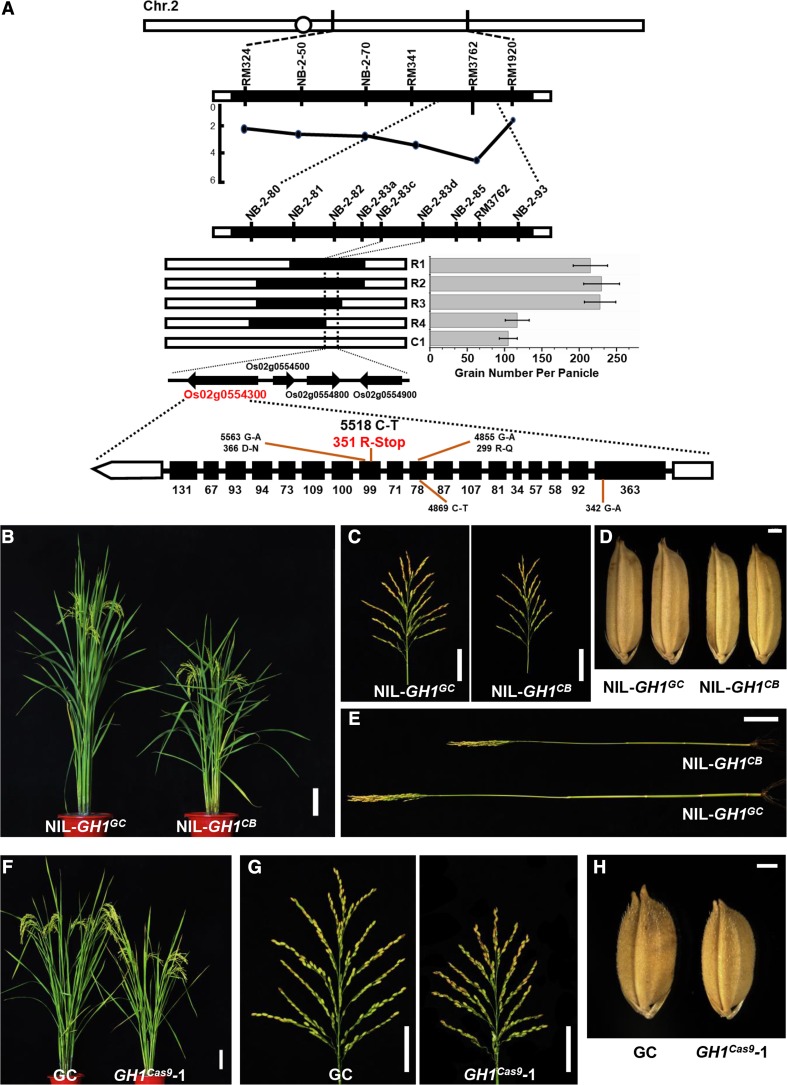
Figure 1.
GH1 contributes to rice plant and panicle development. A, Map-based cloning of GH1. Grain number per panicle of the three recombinant lines (R1–R3) was higher than that of recombinant line R4 and the control (C1, homozygous for CB in the target region; n = 15 plants). Values represent means ± sd. Black and white bars represent homozygous chromosomal segments for GC and CB, respectively. Four open reading frames were found in the candidate region, Os02g0554300, Os02g0554500, Os02g0554800, and Os02g0554900. Sequencing of the full length of the four genes revealed a C-T mutation in the 11th exon of Os02g0554300, resulting in premature stop of this protein. B, Plant architecture of NIL-GH1GC and NIL-GH1CB at the reproductive phase. Bar = 10 cm. C, Mature panicles of NIL-GH1GC and NIL-GH1CB. Bars = 5 cm. D, Mature grains from NIL-GH1GC and NIL-GH1CB. Bar = 1 mm. E, The culms of NIL-GH1GC and NIL-GH1CB. Bar = 5 cm. F, Plant architecture of GC and GH1cas9-1 at the reproductive phase. Bar = 10 cm. G, Mature panicles of GC and GH1cas9-1. Bars = 5 cm. H, Mature grains of GC and GH1cas9-1. Bar = 1 mm.