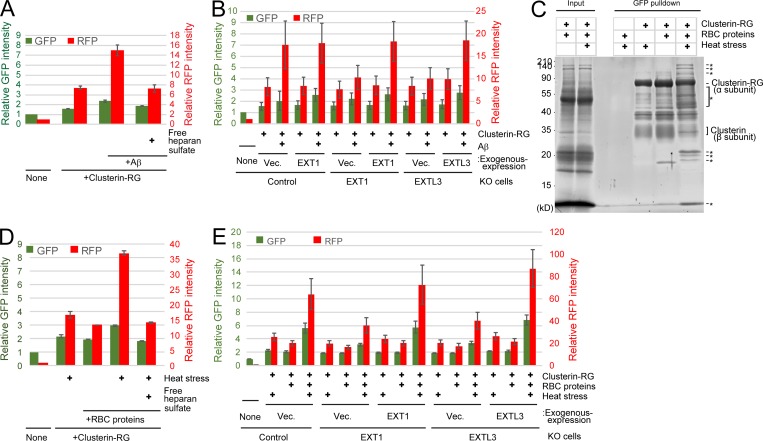
Figure 6.
The Clusterin–HS pathway is a universal degradation system for a wide variety of substrates. (A) Clusterin–HS pathway–dependent Aβ degradation. Purified CluRG was mixed with or without recombinant Aβ in serum-free medium and preincubated at 37°C. HEK293 cells were cultured in medium with or without free HS for 14 h at 37°C and analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) Medium was prepared as in A. Control, EXT1 KO, or EXTL3 KO HEK293 cells (generated by CRISPR) introduced with EXT1, EXTL3, or empty vector (Vec.) were cultured in medium for 14 h at 37°C and analyzed by flow cytometry. The bar graph shows the relative fluorescence intensities (GFP, green left axis; RFP, red right axis) in the cells normalized to that in nontreated cells (n = 3). The data are presented as mean ± SEM. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of CluRG with various RBC proteins. Purified CluRG was mixed with or without RBC proteins and preincubated at 4°C or 50°C for 60 min (heat stress). Samples were subjected to a pulldown assay using an anti-GFP sepharose antibody at 4°C, separated by SDS-PAGE, and detected with SYPRO-Ruby stain. The asterisks indicate heat stress–dependent Clusterin-binding proteins. (D and E) HS is essential for internalization of Clusterin–RBC protein complexes. Purified CluRG was mixed with or without RBC proteins in serum-free medium and preincubated at 50°C for 60 min (heat stress). Control (D), EXT1 KO, or EXTL3 KO (E) HEK293 cells introduced with EXT1, EXTL3, or empty vector were cultured in medium with or without free HS for 14 h at 37°C and analyzed by flow cytometry. The bar graph shows the relative fluorescence intensity (GFP, green left axis; RFP, red right axis) in the cells normalized to that in nontreated cells (n = 3). The data are presented as mean ± SEM.