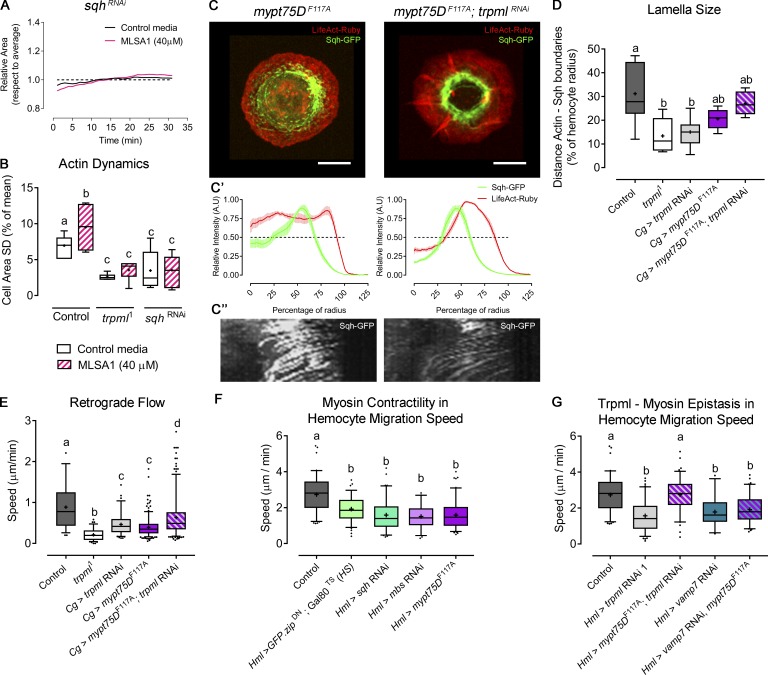
Figure 6.
Myo-II activation rescues trpml phenotype in cytoskeleton and hemocyte migration. (A) Cell dynamics in response to MLSA1 treatment in sqh-deficient hemocytes. Data are shown as changes in area over time with respect to average (dashed line). (B) Actin dynamics quantified as SD of the area over time (n = 3 independent cultures, n ≥ 4 cells/condition, 30-min movies, 1-min intervals). Full videos are included in Video 2. (C) Representative images of hemocytes expressing LifeAct-Ruby and sqh-GFP in the conditions mypt75DF117A and trpml RNAi with mypt75DF117A. Scale bar: 5 µm. (C’) Graphical distribution of LifeAct-Ruby and Sqh-GFP with respect to cell radius. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. A.U., arbitrary units. The dashed line marks the 50% of the maximal signal intensity. (C'') Kymographs showing Sqh-GFP retrograde flow over time (30 time points, one frame per minute): mypt75DF117A (left) and trpml RNAi with mypt75DF117A (right). (D) Quantification of lamella size with respect to the radius (n = 3 independent cultures, n ≥ 3 cells/condition, 30 time points, 360°/cell). (E) Quantification of Sqh-GFP retrograde flow speed (n = 3 independent cultures, n ≥ 3 cells/condition). Full videos are included in Video 5. (F) Pupal hemocyte migration speed showing that both increased and deficient Myo-II activity significantly decreases migration speed (n ≥ 3 animals/condition, n > 20 cells/animal). (G) Pupal hemocyte migration speed showing that mypt75DF114A rescues the speed in trpml- but not in vamp7-deficient hemocytes (n ≥ 3 animals/condition, n > 20 cells/animal). The values in B, D, and E–G are presented as box and whiskers (5%–95% in E–G), one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons post hoc test. Mean values are indicated as “+”; statistically equivalent values are represented with the same letter (P < 0.05). Hml and Cg stand for hemolectin and collagen Gal4 drivers, respectively. DN, dominant-negative; TS, thermo-sensitive; HS, heat shock.