Figure 1.
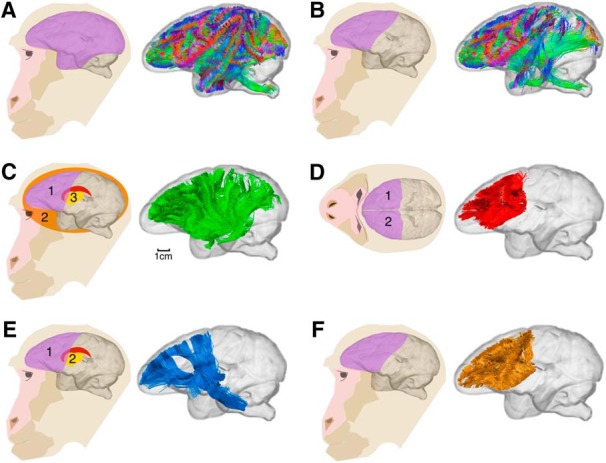
Pipeline for dissection of the association, commissural, projection, and intrafrontal tracts, illustrated in a single macaque brain. A, An inclusion region of the whole left or right hemisphere was used to extract all hemispheric connections. Exclusion regions (not pictured) were used to remove artifactual streamlines coursing through the contralateral internal, external, and extreme capsules. B, From the set of streamlines in each hemisphere defined in A, an inclusion region of the frontal lobe was used to select only streamlines passing through the frontal lobe, including those extending between frontal and nonfrontal regions. C–F, These frontal lobe connections were then further separated into the following groups: association fibers, using an inclusion region of the frontal lobe (1) and exclusion regions in the midsagittal section (2) and subcortical nuclei (3); C); commissural fibers, using the two frontal lobes (1, 2) as inclusion regions (D); projection fibers, using one inclusion region of the frontal lobe (1) and one in the brainstem, thalamus and internal capsule (2; E); and intrafrontal association fibers (F). Intrafrontal fibers were defined with the condition that both ends of the streamline must be within the frontal lobe region of interest. The same approach was used in all species.
