Fig. 3.
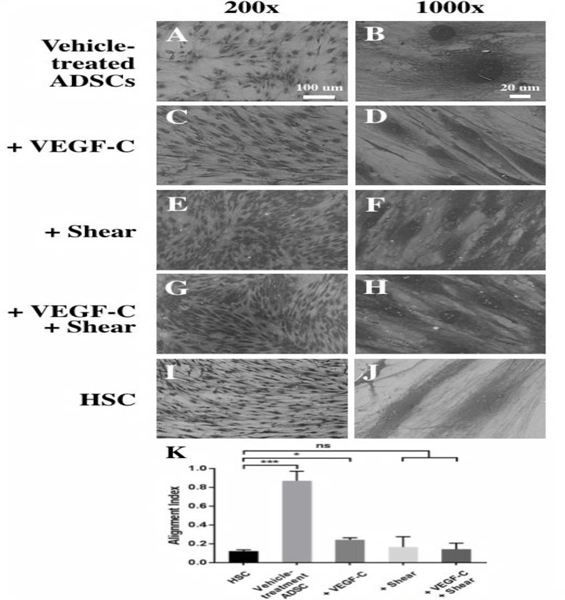
Differentiation of ADSCs into Schlemm’s canal-like cells induced by VEGF-C and shear stress for 11 days. SEM images of ADSCs at 200× (A, C, E, G, I) and 1000× (B, D, F, H, J) showed dramatic changes in cell morphology and orientation. Vehicle-treated ADSCs (A, B), ADSCs treated with VEGF- C (C, D), shear stress (E, F), or with VEGF-C under shear stress (G, H), and primary HSC cells as the positive control (I, J). Scale bars: (A, C, E, G, I) 100 μm, (B, D, F, H, J) 20 μm. (K) Quantitative analysis of the degree of cell orientation based on the alignment index. A high alignment index represents high randomness of cell orientation. HSCs and differentiated ADSCs are much more oriented than vehicle-treated ADSCs. *p < 0.01, ***p <0.0005, ns: not significant.
