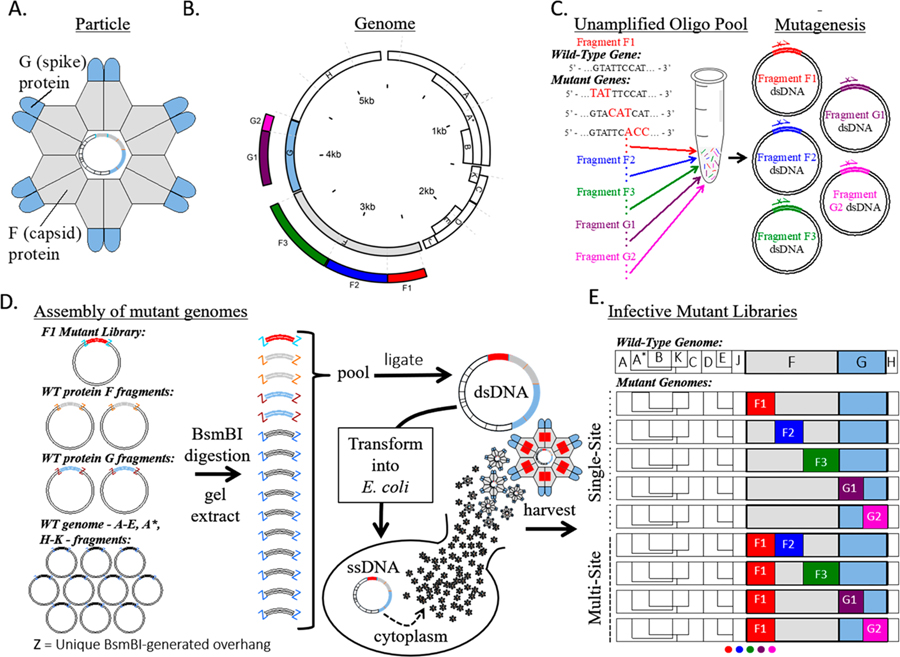
Figure 1.
ΦX174 mutant library assembly. (A) Cartoon structure of the ΦX174 virion. F and G proteins are organized into pentamers and are the only exposed proteins in the mature virion. (B) A schematic of the circular ΦX174 genome showing the size and location of the synthetic genome fragments. The locations of mutated residues in genes F and G are indicated. (C) An oligo pool containing all mutagenic oligos for genes F and G was generated and used in Nicking Scanning Mutagenesis for the generation of saturation mutant libraries for genes F and G. (D) Golden Gate cloning was used to assemble the mutant genomes, which were transformed into XL1-Blue competent cells (Agilent) and plated on susceptible E. coli C cells. The resulting plaques were sequenced. (E) Linear schematics depicting some of the possible mutant libraries that can be generated using the workflow and existing libraries.