Figure 3. The Na+/K+-ATPase pump is required for creatine uptake by Myl-R cells.
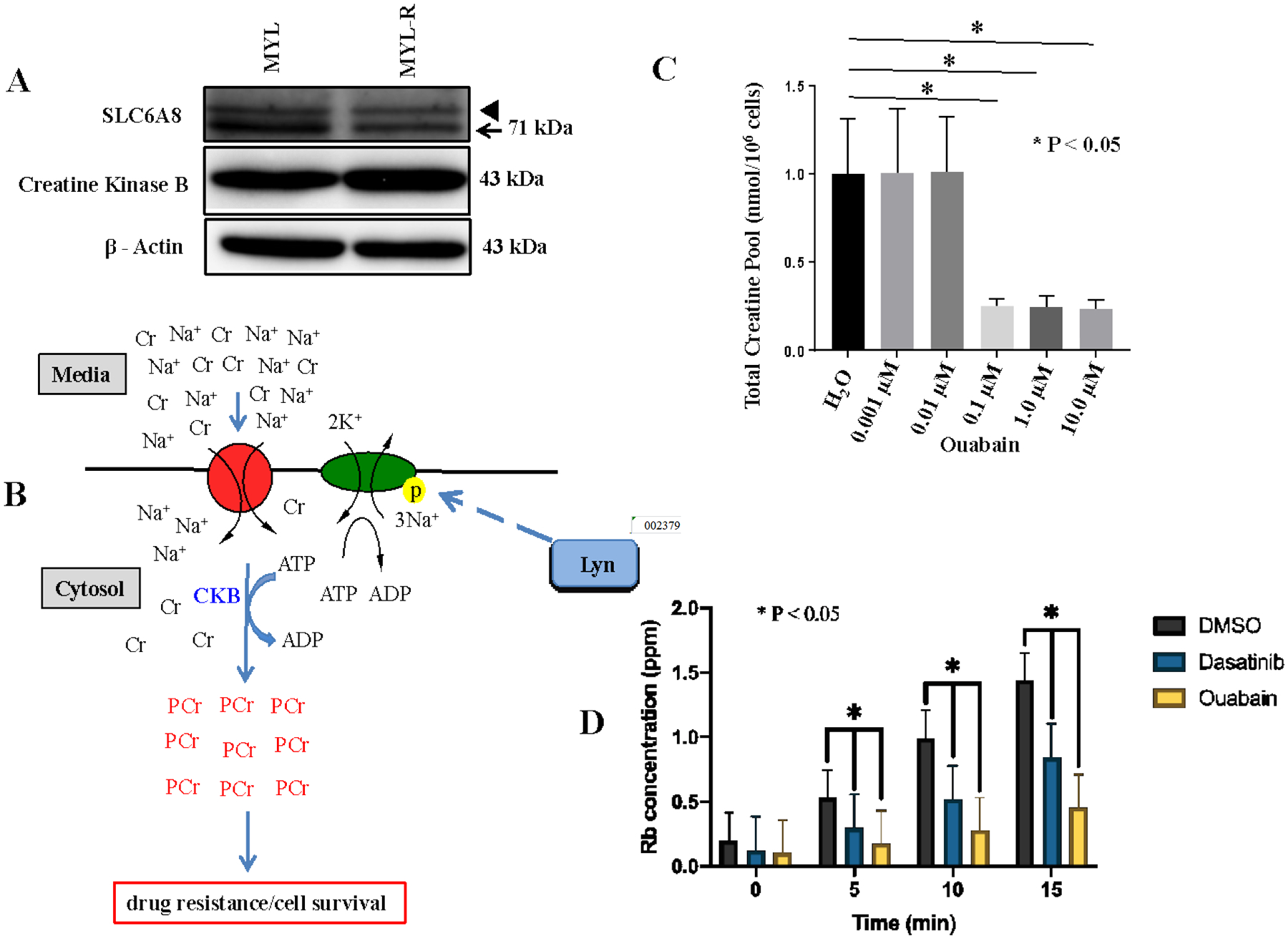
(A) Creatine kinase B (CKB) and SLC6A8 protein levels were compared in Myl and Myl-R cells by Western blotting. Arrowhead represents cross reactivity with an off-target protein of unknown origin. (B) A model diagram depicting creatine uptake and subsequent phosphorylation by CKB to generate phosphocreatine. (C) Treatment of Myl-R cells with increasing concentrations of ouabain significantly reduced total intracellular creatine in a dose-dependent manner as determined by 1H NMR analysis. Myl-R cells were treated for 24 hours with increasing concentrations of ouabain and 1H NMR used to measure total creatine. (D) Treatment of Myl-R cells with dasatinib (1 nM) or ouabain (100 nM) significantly reduced rubidium (Rb) uptake as determined using the Rb uptake assay. Rb+ uptake measurements were performed courtesy of Dr. Andrew Ghio’s lab (EPA, UNC Chapel Hill, NC). The data presented in this figure are averages of three independent experiments, and * represents p < 0.05.
