Figure 4. Lyn regulates the Na+/K+-ATPase phosphorylation and creatine uptake in Myl-R cells.
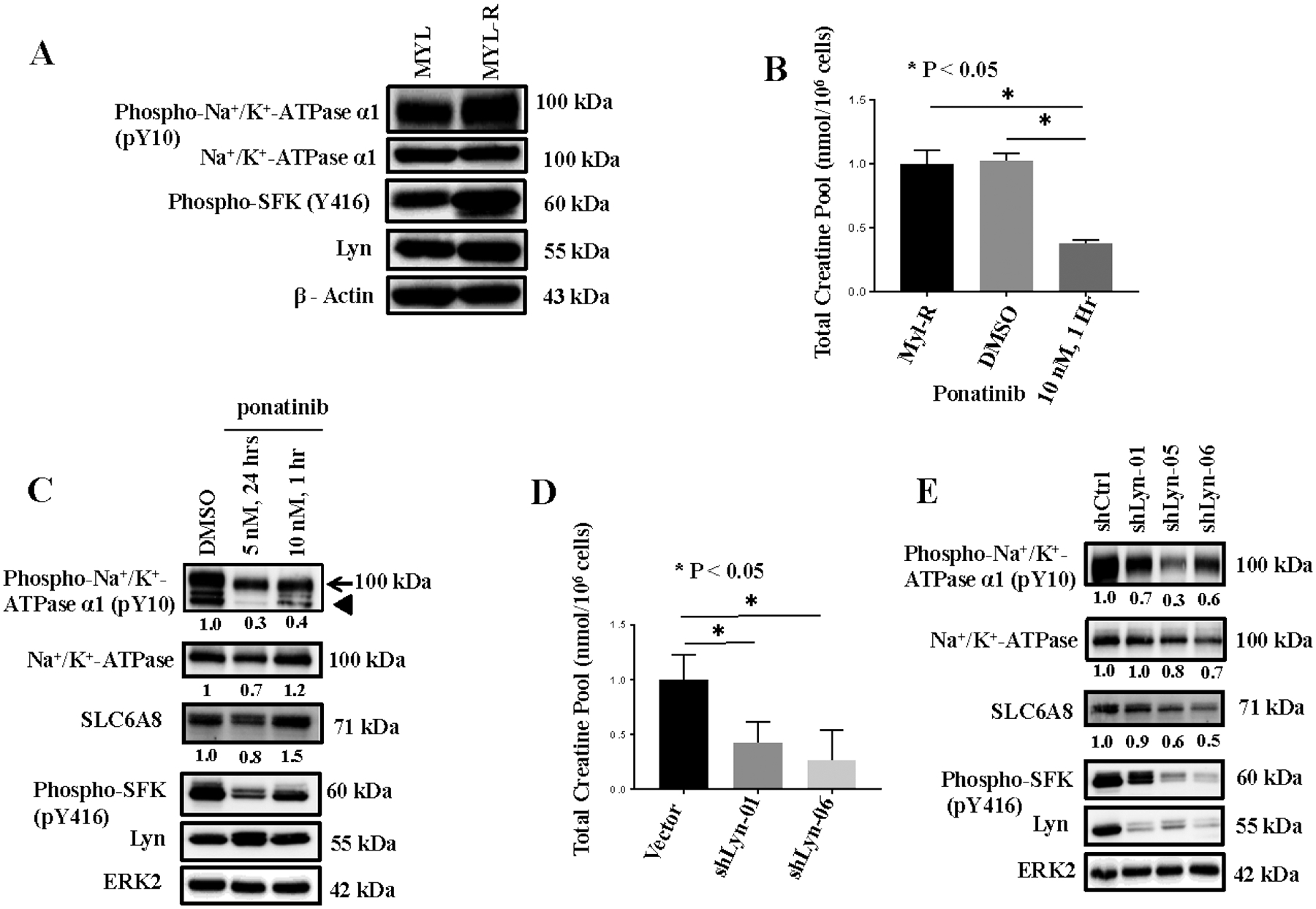
(A) Western blotting showed that tyrosine phosphorylation of Lyn and the Na+/K+-ATPase was higher in Myl-R compared to Myl cells. (B) Lyn inhibition significantly reduced the total creatine pool in Myl-R cells. Approximately 15 × 106 Myl-R cells were treated for 1 hour with DMSO or ponatinib (10 nM) and total intracellular creatine determined using 1H NMR as outlined in Materials and Methods. Control (DMSO) Myl-R cells were similarly analyzed for comparison. (C) Western blotting confirmed that Lyn inhibition reduced the phosphorylation of Lyn (pY416) and the Na+/K+-ATPase (pY10). Arrowhead represents cross reactivity with an induced 75–80 kDa off-target protein of unknown origin. (D and E) Lyn knockdown significantly reduced Na+/K+-ATPase phosphorylation and the total intracellular creatine pool in Myl-R cells. Approximately 15 × 106 Myl-R cells were infected with lentiviral particles containing shRNA directed against Lyn (shLyn-01, shLyn-06) and intracellular creatine levels measured. Lyn shRNA constructs (shLyn-01, shLyn-05, and shLyn-06) reduced Na+/K+-ATPase and Lyn phosphorylation. The data are the averages of three independent experiments, and * represents p < 0.05.
