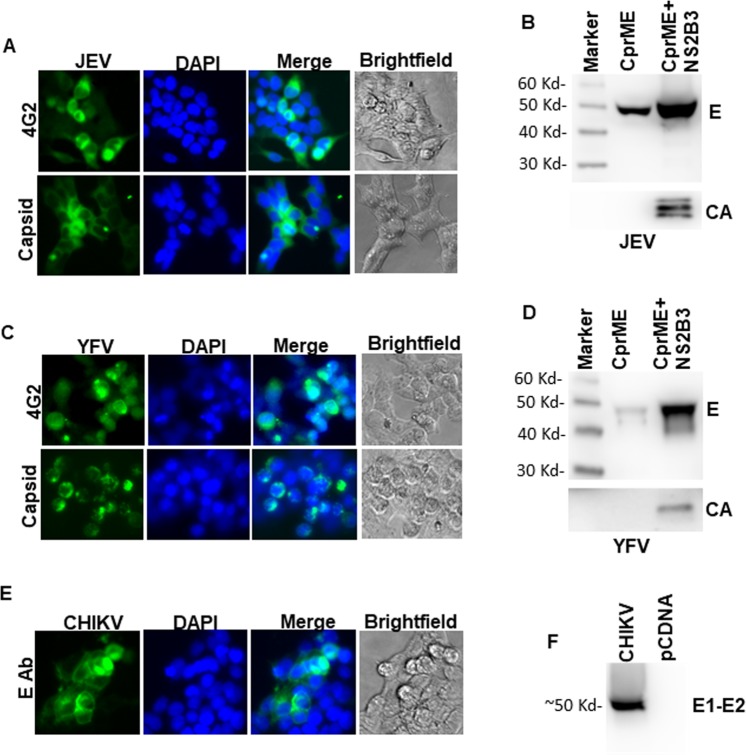
Figure 1.
Characterization of JEV, YFV and CHKV protein expression and VLP release. (A) 293 T cells were transfected with JEV CprME expression vector. Cells were analyzed for E protein and Capsid protein expression after staining with respective antibodies followed by fluorescence microscopy. (B) 293 T cells were transfected with JEV CprME expression vector alone or the JEV CprME vector along with Zika NS2B-3 expression plasmid. Culture supernatants were ultracentrifuged and analyzed for E protein and Capsid protein expression by western blotting. (C) 293 T cells were transfected with YFV CprME expression vector and analyzed for E protein and Capsid protein expression by immunofluorescence microscopy. (D) 293 T cells were transfected with YFV CprME expression vector alone or the YFV CprME vector along with Zika NS2B-3 expression plasmid. Culture supernatants were ultracentrifuged and analyzed for E protein and Capsid protein expression by western blotting. (E) 293 T cells were transfected with CHKV expression vector and analyzed for E1-E2 protein expression by immunofluorescence microscopy. (F) 293 T cells were transfected with CHKV expression vector. Culture supernatants were ultracentrifuged and analyzed for E1-E2 protein expression by western blotting. Images A, C and E were analyzed using NIS Elements AR software version 3.2 (Nikon; https://nis-elements-viewer.software.informer.com/3.2/). Images B, D and F were analyzed using GENETOOLS gel analysis Software version 4.03 (f) (Syngene, https://www.syngene.com/software/genetools-automatic-image-analysis/).