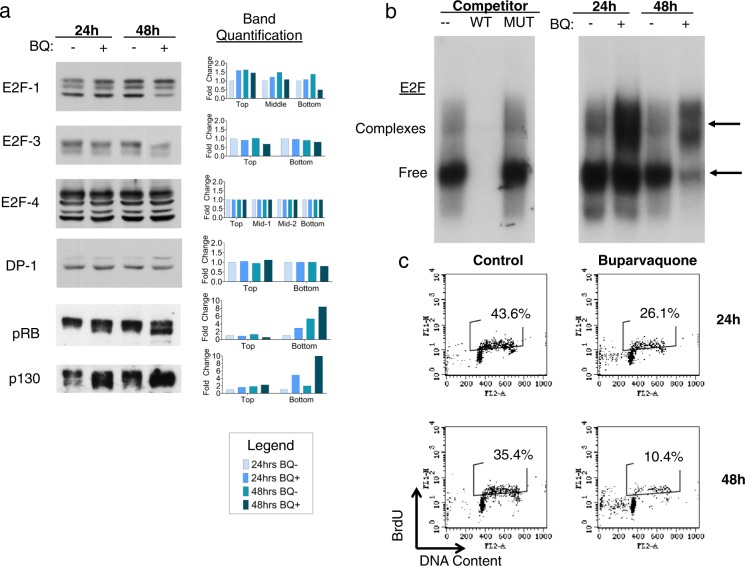
Figure 2.
RB/E2F signaling is activated by Theileria parasites. (a) Western blot analysis (left) of E2F-1, E2F-3 E2F-4, DP-1, pRB, and p130 expression in TpMD409B.2 cells, either left untreated (−), or treated (+) for 24 h and 48 h with buparvaquone (BQ), including band intensity quantification (right). Shown are representatives of three independent experiments. (b) E2F DNA binding activity in TpMD409B.2 cells was assayed by EMSA using gP32- labeled double-stranded oligonucleotide spanning E2F binding sites from the dhfr gene promoter. Left panel, nuclear extracts from TpMD409B.2 cells were incubated with γP32-labeled probe in absence or presence of a 100 fold molar excess of unlabeled wild type (WT), or mutated (MUT) double-stranded oligonucleotide. Binding reactions were resolved by non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel, which was processed afterwards for autoradiography. Right panel, EMSA analysis of E2F DNA binding activity in nuclear extracts from untreated, proliferating TpMD409B.2 cells (−) and TpMD409B.2 cells treated for 24 and 48 h with the parasiticidal drug buparvaquone (+). Arrows indicate E2F in complex with RB family proteins (Complexes) or free E2F protein (Free). (c) Flow cytometric analysis of BrdU incorporation and DNA content in TpMD409B.2 cells, either left untreated (control), or treated with buparvaquone for 24 h and 48 h. Shown is a representative of three independent experiments.