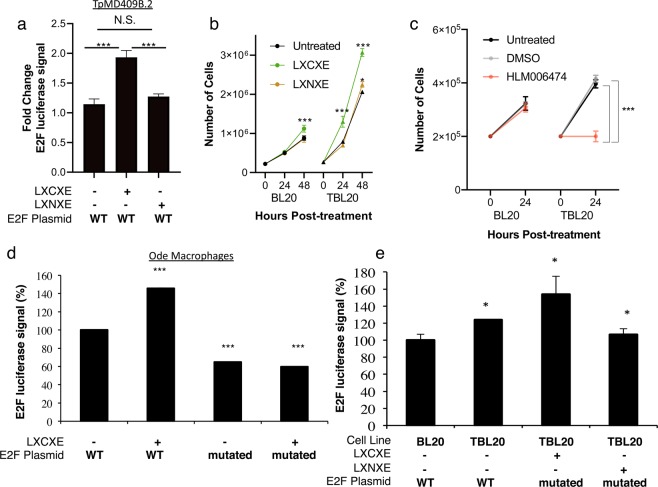
Figure 3.
Sequence-specific disruption of RB/E2F signaling with cell permeating peptides reveals the active role of E2F signaling during Theileria infection. (a) TpMD409B.2 cells were transfected with E2F-luc (WT = wild-type E2F binding construct), or mutated E2F-luc constructs (labeled ‘mutated’) together with a CMV-lacZ plasmid to normalize for transfection efficiency. Luciferase and β-galactosidase activities were measured 24 hrs after transfection. E2F-luc relative luciferase activity normalized to mE2F-luc. Shown is the average of 3 independent experiments with standard deviation. BL20 or TBL20 cells were treated with (b) 1μM of penetrating peptides (VKKKKIKREIKIYIEEVFTPLVLKCKELK-K(FITC)) containing the TpGcpE LXCXE motif, or an LXNXE control (VKKKKIKREIKIYIEEVFTPLVLKNKELK-K(FITC)) or (c) E2F inhibitor or DMSO control, and then counted by hemacytometer after the indicated timepoints. Shown is the average of 3 independent experiments with standard deviation. Then, either (d) virulent Ode T. annulata-transformed macrophages, or (e) BL20/TBL20 T. annulata-transformed cells were transfected with E2F-luc plasmid (or mutated E2F-luc as in (c)) and incubated for 24 hrs at 37 °C. Then, cells were treated with penetrating peptides as in (b) for 2 hrs and luciferase activity was quantified. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments done with biological duplicates, with mean + standard deviation (*P-value < 0.05 compared to untreated; ‡P-value < 0.05 compared to its respective BL20 control).