Figure 4.
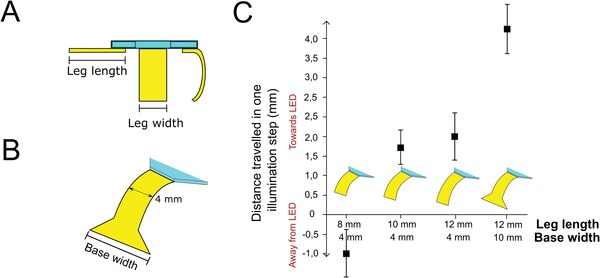
Investigation of the importance of leg dimension and shape for locomotion. A) Schematic depiction of the robot, showing leg length and width dimensions. B) Schematic drawing of the leg design with a wider leg base which enhances walking locomotion. C) The effect of leg length and width on both the directionality and efficiency of locomotion. We plot the average distance covered by one illumination cycle (described in Figure 3B) for robots with varying leg dimensions and the standard deviation of these values for ≈10 steps. We observe that short 8 mm legs result in walking in a direction away from the illumination and longer, 10 and 12 mm legs, in locomotion toward the light source. Little variation is observed between legs of 10 and 12 mm, yet an increase in leg base largely increases the distance covered by one stride.
