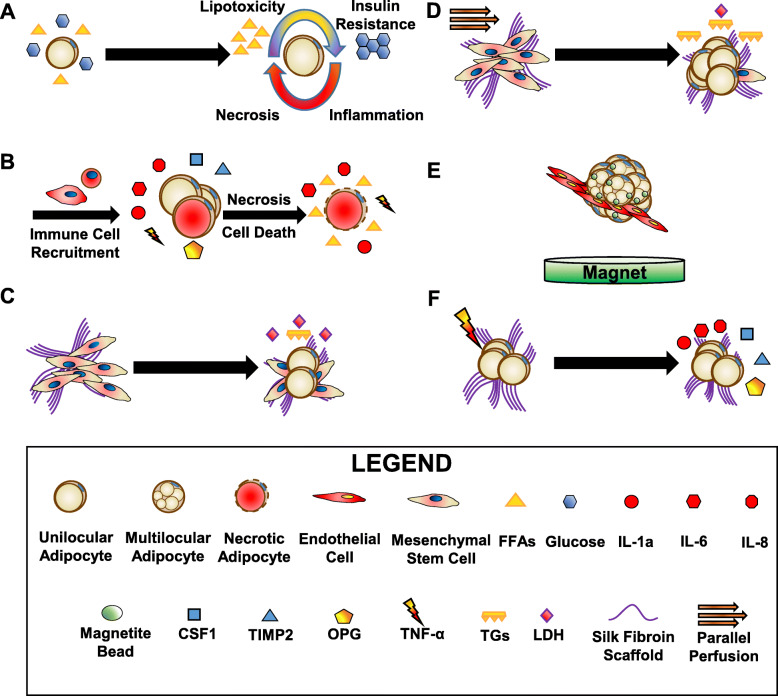
Fig. 2.
Overview of the effects of obesity on adipocytes and 3D tissue-engineered adipose models of obesity. a During obesity, excess calories (whether from free fatty acids (FFAs) or glucose) cause adipocytes to become hypertrophic. The increase in FFAs causes activation of oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and subsequent secretion of cytokines and adipokines. Oxidative and ER stress cause insulin resistance by negatively regulating insulin signaling. As inflammation and adipocyte size increase, oxygen is unable to penetrate the adipose tissue causing hypoxia, necrosis and eventually cell death. b Hypertrophic adipocytes secrete chemokines (C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), CCL8, CCL5, colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF1)) and cytokines that attract immune cells, mainly macrophages. Adipose tissue macrophages can secrete anti-inflammatory factors (interleukin-10 (IL-10) and IL-1) and pro-inflammatory factors (tumor necrosis factor α, (TNF-α), IL-6 and IL-1β). Inflammation can cause necrosis and cell death, further releasing pro-inflammatory molecules like cytokines and excess lipids, perpetuating the cycle of chronic low-grade inflammation. c and d Bellas et al. 2013 and Abbott et al. 2015 both demonstrated the benefits of perfusion (d, yellow-orange arrows) compared to static culture (c) for human mesenchymal stem cell (hMSC)-derived adipocytes differentiated on silk fibroin scaffolds (e.g. increased differentiation, triacylglycerols (TGs), and viable culture time, and decreased the damage-associated protein, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)). e Daquinag et al. 2013 co-cultured 3 T3-L1 preadipocytes with the endothelial cell line bEND.3 embedded with magnetite nanoparticles. f Abbott et al. 2016 obtained adipocyte-derived stem cells from lipoaspirates and seeded and differentiated these cells on silk scaffolds. These cultures secreted factors found in both obesity (IL1-α, osteoprotegerin (OPG), and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 2 (TIMP2)) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (IL-6 and IL-8)