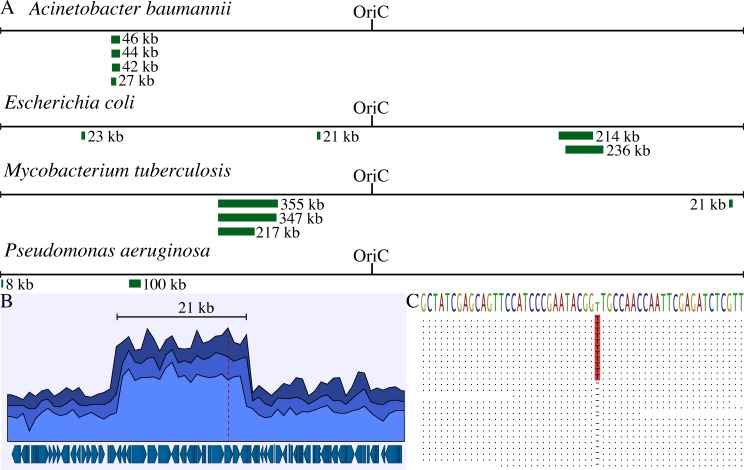
Fig 4. Duplications identified in natural isolates of A. baumannii, E. coli, M. tuberculosis, and P. aeruginosa.
(A) One hundred whole genome sequences per species were downloaded from the SRA and analysed for regions with increased coverage. Duplicated regions are indicated with green bars and represent unique segments of the chromosomes. (B) Read coverage analysis of a chromosomal section within the M. tuberculosis isolate with a 21 kb duplication. The blue shades (top to bottom) represent the maximum, average and minimum read coverage on a sliding 1 kb window. Genes within the chromosomal segment are indicated below. The duplicated region contains 21 genes and the frameshift mutation that is present in one copy of the glutamine synthetase gene is indicated with a dotted red line. (C) Sequence analysis of the frameshift insertion within the glutamine synthetase gene (~25% of reads shown). The consensus sequence is shown as sequence logo on the top with the reads below. Residues in the reads that match the reference are shown as dots. The insertion of a thymine is indicated in red. The site of the insertion has a 155-fold coverage and the frameshift present in 49% of reads.