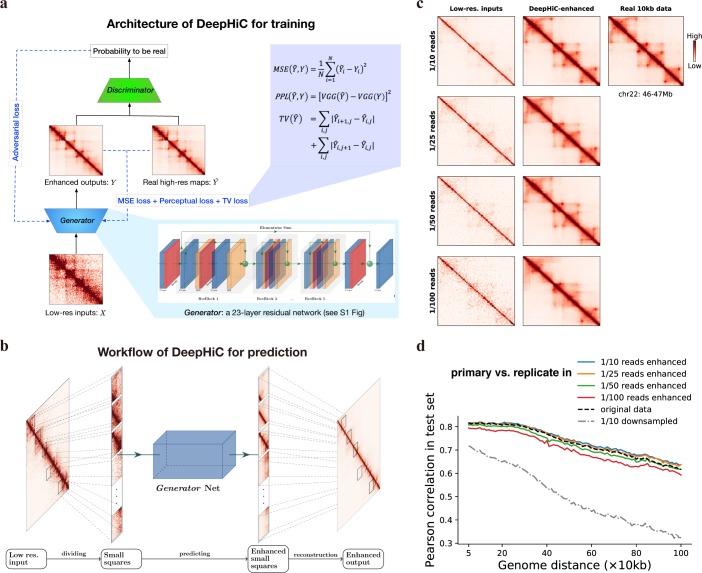
Fig 1. Overview of the DeepHiC.
(a) DeepHiC framework: low-resolution inputs are obtained by randomly downsampling original reads. It imputes enhanced contact maps using a 23-layer residual network called Generator. In the training process, the enhanced outputs are approaching real high-resolution matrices by minimizing mean square error (MSE) loss, perceptual loss (PPL), and total variation (TV) loss, meanwhile, a Discriminator network distinguishes enhanced outputs from the real ones and reports the probabilities of enhanced outputs to be real to the Generator through adversarial (AD) loss. The imputation and discrimination steps form the adversarial training process. (b) For prediction, a low-resolution Hi-C matrix is divided into small squares as inputs. Then enhanced small squares are predicted by the Generator. Finally, those squares are merged into a chromosome-wide contact map as the enhanced output. (c, d) We randomly downsampled the original reads (obtained from GEO GSE63525) to 1/10, 1/25, 1/50, and 1/100 reads to simulate low-resolution inputs. DeepHiC is trained on chromosomes 1–14 and tested on chromosomes 15–22 (i.e., test set), in GM12878 cell line. (c) The trained DeepHiC model can be used for enhancing low-coverage sequencing Hi-C data, as an example which shows a 1Mb-width sub-region on chromosome 22 and (d) obtain high correlations between DeepHiC-enhanced matrices and real high-resolution Hi-C at each genomic distance. Colorbar setting: see S1 Note.