fig 1.
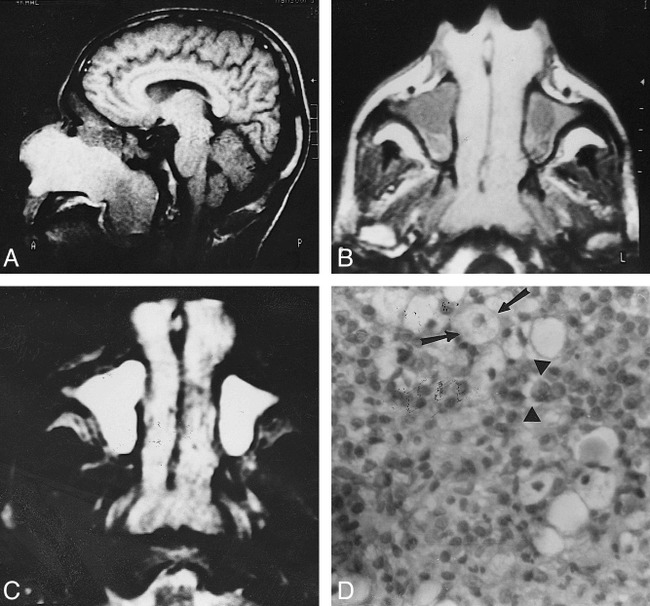
Bilateral symmetrical rhinoscleroma.
A, Sagittal T1-weighted image (600/20) shows a large nasal mass with striking high signal intensity extending through the posterior choanae into the nasopharynx.
B, Axial T1-weighted image (600/20) shows bilateral, symmetrical nasal masses of homogeneous signal intensity. They are hyperintense relative to muscle but less hyperintense than fat. They extend through the anterior nares and posterior choanae. Hypointense fluid is seen in both maxillary sinuses.
C, Axial T2-weighted image (2500/80) shows the nasal masses are hyperintense relative to fat and muscle but less hyperintense than retained fluid. Small areas of hypointensity are present.
D, Photomicrograph of a resected specimen. Many Mikulicz cells (arrows) are present with scattered Russell bodies (arrowheads) and many plasma cells (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnification ×400).
