fig 2.
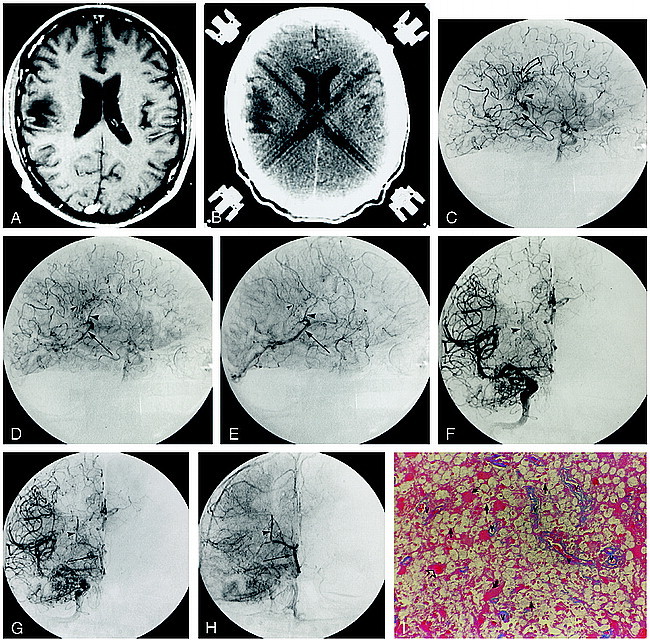
Patient 2.
A, Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR image (600/14/2) illustrates the nonenhancing right posterior frontal lesion.
B, Corresponding contrast-enhanced CT scan shows a hypodense deep and subcortical white matter lesion.
C–E, Late arterial (C), capillary (D), and early venous (E) phase digital subtraction angiographic (DSA) images (lateral projection) from the accompanying right internal carotid artery (ICA) angiogram depict a region of arteriovenous shunting corresponding to the location of the MR abnormality. A dense parenchymal blush is evident throughout the inferior frontoparietal region (curved arrow, C). Arteriovenous shunting results in the early opacification of a direct atrial vein (large arrowhead) and the posterior third of the right internal cerebral vein (arrow). An early draining cortical parietal vein is seen in D and E (small arrowhead).
F–H, Corresponding mid-arterial (F), late arterial (G), and early venous (H) phase frontal DSA images confirm early opacification of the atrial (arrowhead) and right internal cerebral (arrow) veins.
I, Histologic section shows several vascular channels (v) without evidence of reduplication of the basal lamina. There is mingling of numerous histiocytes (straight arrows) and reactive astrocytes (curved arrows), characteristic of a demyelinating process. Some of the astrocytic cells have enlarged hyperplastic nuclei (open arrows) often seen in PML (azocarmine stain, original magnification ×100).
