fig 1.
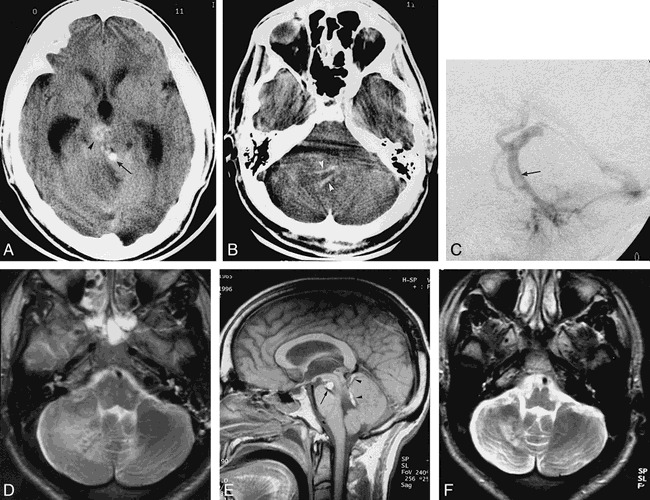
31-year-old man with severe headache, vomiting, ataxia, and right-sided facial palsy.
A, Unenhanced CT scan at the level of the midbrain shows a spontaneously dense tubular structure (arrow) in front of the vermis, later proved to be the thrombus in the DVA collector. Arrowhead points to the cavernous angioma. There is edema of the right cerebellum and secondary obstructive hydrocephalus.
B, Unenhanced CT scan at the level of the pons shows tubular high-density structures (arrowheads) corresponding to the thrombus in the branches of the DVA.
C, Late venous phase of left vertebral arteriogram proves the presence of a clot inside the DVA collector (arrow).
D, Axial T2-weighed MR image at the level of the pontomedullary junction reveals nonhemorrhagic subcortical infarction of the right cerebellum.
E, On unenhanced sagittal T1-weighed MR image, high signal intensity corresponds to subacute clot inside the DVA collector (arrowheads) and correlates well with angiographic findings (C). Arrow points to the midbrain cavernous angioma.
F, Axial T2-weighed MR image obtained in April 1998 confirms the subcortical infarction.
