fig 2.
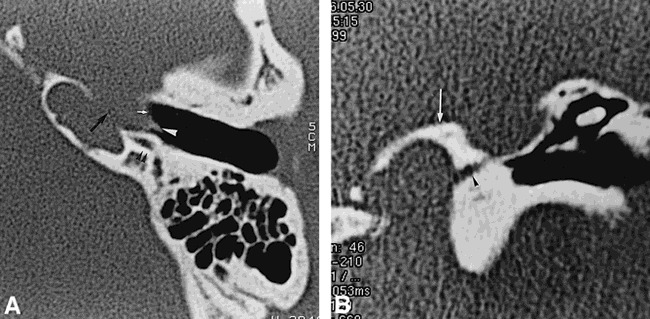
Case 2: 16-year-old boy, brother of girl in case 1, also with profound bilateral congenital sensorineural hearing loss.
A, Axial CT scan shows an aberrant course of the left internal carotid artery, which bulges into the middle ear (white arrow). Dehiscence of the lateral wall of the petrous bone adjacent to the horizontal carotid artery is present (black arrow). A small lateral tract corresponds to a persistent stapediohyoid artery (white arrowhead). The facial nerve passes behind the internal carotid artery (black arrowheads).
B, Coronal CT scan shows enlargement of inferior tympanic canaliculus (arrowhead). Arrow indicates jugular foramen.
