fig 5.
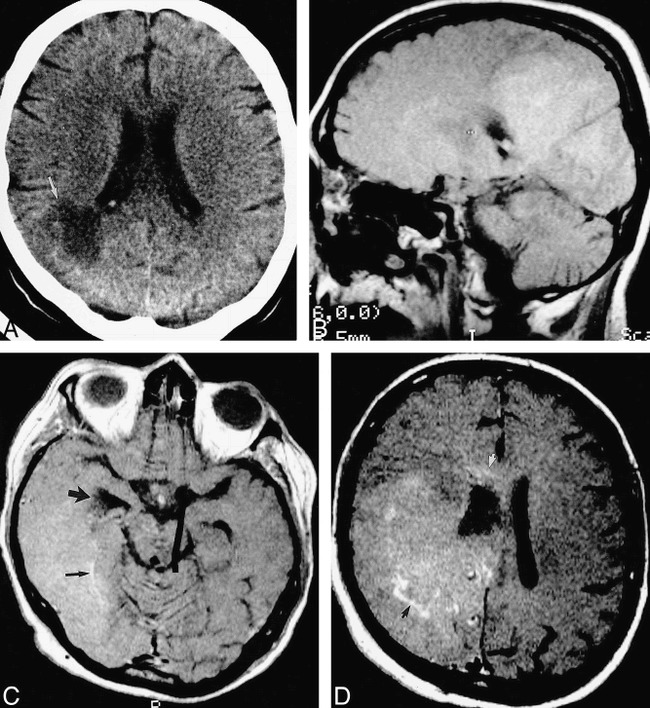
40-year-old woman after simultaneous pancreas/kidney transplantation had mental status decline and, later, a left homonymous hemianopia.
A, Axial unenhanced CT scan shows a large low-attenuation lesion (arrow) extending to the right lateral ventricle.
B, Parasagittal unenhanced spin-echo T1-weighted (630/20/2) MR image 10 days later shows a large, confluent area of diffuse, mild hyperintensity, suggesting petechial hemorrhage.
C, Axial contrast-enhanced T1-weighted (450/20/2) MR image shows involvement of the temporal and occipital lobes. The right temporal horn is obstructed (large arrow). There are serpentine foci of enhancement (small arrow).
D, Axial contrast-enhanced T1-weighted (450/20/2) MR image superior to C shows involvement of the frontal and parietal lobes, with focal areas of enhancement (black arrow). The abnormality extends into the corpus callosum (white arrow). The patient died 2 days later. At autopsy, this large abnormality was found to be Aspergillus cerebritis with scattered areas of petechial hemorrhage.
