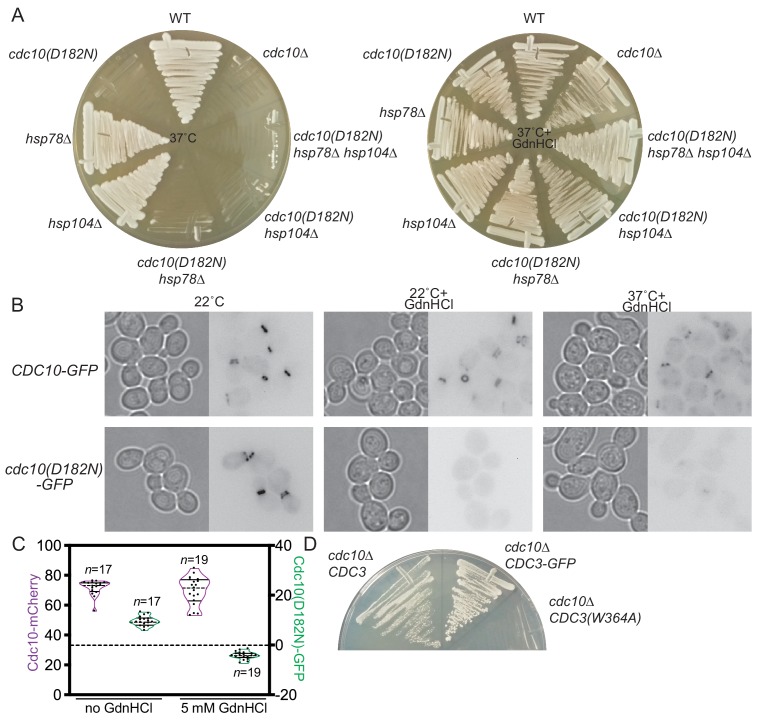
Figure 2. GdnHCl promotes exclusion of mutant Cdc10 molecules from higher-order septin assemblies.
(A) As in Figure 1B, but with the addition of cdc10∆ cells, and the cells were streaked with a toothpick, rather than spotted from dilutions. (B) Cultures of the strains JTY3985 (‘CDC10-GFP’) or JTY3986 (‘cdc10(D182N)-GFP’) were grown overnight in liquid culture at the indicated temperatures with or without 3 mM GdnHCl and then imaged by microscopy with transmitted light (left images) or for GFP fluorescence (right images). Fluorescence images were inverted to improve visibility. (C) Cells of the strain JTY4020 were cultured at 37°C with or without 5 mM GdnHCl and imaged as in (B), then line scans of bud neck fluorescence were performed for the indicated numbers of cells to quantify levels of Cdc10-mCherry (purple) or Cdc10(D182N)-GFP (green). For each data point, cytosolic signal was subtracted from bud neck signal; negative values thus indicate cytosolic signal greater than septin ring signal. In violin plots, solid lines indicate quartiles and dashed lines are medians. (D) In strain JTY5104, the chromosomal sources of Cdc3 and Cdc10 are eliminated by deletion and Cdc3(W364A) and Cdc10 are supplied by LYS2- or URA3-marked plasmids, respectively. Following introduction of LEU2-marked plasmid encoding WT Cdc3 (pFM831) or Cdc3-GFP (pML109), the transformants were passaged on medium with α-aminoadipate to select for loss of the CDC3(W364A) plasmid. These clones were then streaked, along with cells of the original strain JTY5104 carrying both plasmids (‘cdc10∆ CDC3(W364A)”), on medium with 3 mM GdnHCl and 5-fluoro-orotic acid (FOA, to select for loss of the CDC10 plasmid) and incubated for 4 days at 22°C.