Fig. 1. A mutational scan for the surface expression of rhodopsin variants.
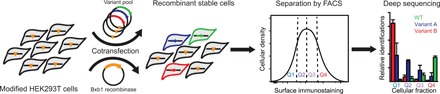
A cartoon depicts the general workflow for the deep mutational scanning assay described herein. A pool of stable cells expressing single rhodopsin variants from a common genomic locus is first produced by cotransfecting a plasmid library and an expression vector for Bxb1 recombinase (23). Recombined cells are then isolated on the basis of their characteristic bicistronic enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) expression. The stable library is then fractionated according to the surface immunostaining levels of expressed rhodopsin variants using fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). The relative abundance of each variant within each fraction is then evaluated by deep sequencing. Sequencing data are then used to determine the relative surface immunostaining of each variant. HEK293T, human embryonic kidney 293T.
