Fig. 3. Steps in the model.
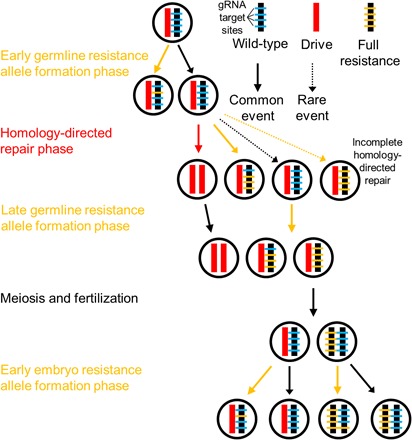
First, wild-type gRNA target sites can be cleaved in the early germline, forming resistance alleles. Next, cleavage occurs at a high rate in the homology-directed repair phase. Usually, this results in successful conversion to a drive allele. However, if homology-directed repair fails to occur, then end joining can form resistance alleles. Incomplete homology-directed repair can also convert the entire allele to a resistance allele, ignoring individual target sites. Next, another resistance allele formation phase converts most remaining wild-type sites into resistance sequences. Meiosis and fertilization take place, and then, if the female parent had at least one drive allele, a final phase of resistance allele formation takes place in the early embryo.
