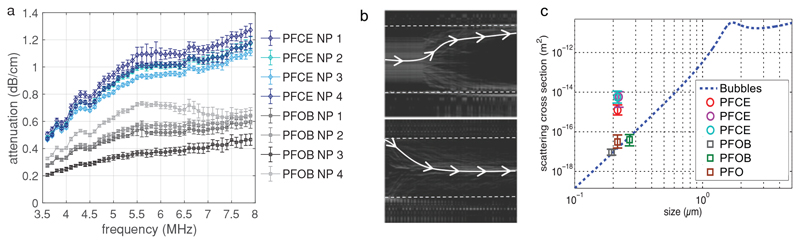
Figure 3.
Acoustic characterization of PFCE-PLGA nanoparticles. a) Attenuation of acoustic waves by nanoparticle solution (10 mg mL−1) at different frequencies. PFCE-loaded nanoparticles display higher attenuation than PFOB-loaded nanoparticles indicating that PFCE nanoparticles display higher scattering intensity. Each line represents an independent batch of nanoparticles; number of the batch corresponds to number in Table S1 (Supporting Information). b) Optical maximum intensity projection images for a sample of PFCE particles (upper) and PFOB particles (lower) flowing in a channel exposed to a standing acoustic wave. PFCE particles move toward high-pressure areas (channel edges indicated) whereas the PFOB particles move toward the pressure nodes located at the center of the channel. A sample path is highlighted in each panel. c) Scattering cross section of various particles compared to coated bubbles, as a function of the size of the particles. A square symbol denotes a positive sign for the radiation force, while circles denote a negative sign. Nanoparticles with PFCE show unexpectedly high scattering cross sections.