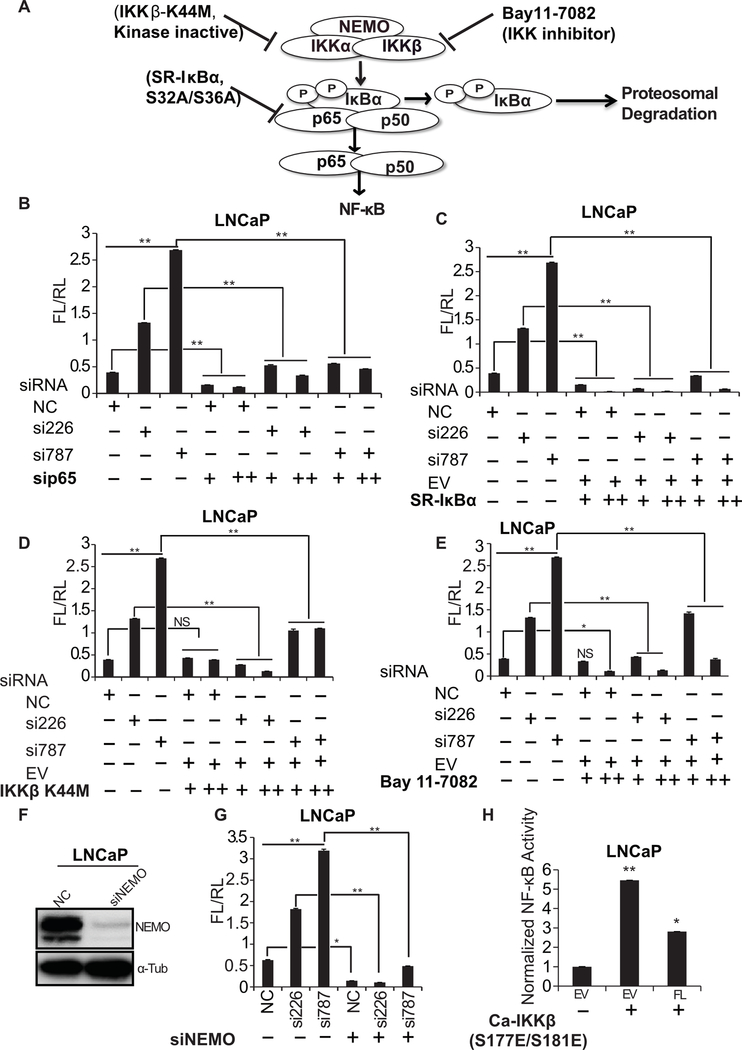
Figure 3. DRAIC represses NF-κB pathway at the level of IKK.
(A) A Schematic representation of the canonical NF-κB pathway with different inhibitory molecules mentioned in this figure. (B-E) NF-κB luciferase reporter activity in LNCaP cells transfected with siRNAs (50 nM) against DRAIC followed by either co-transfection of si-p65 (25 nM and 50 nM) (B), overexpression of super repressive IκBα (C), overexpression of dominant negative IKKβ (K44M) (D), or, inhibition of IKK by Bay11–7082 (E). EV: empty vector. (F) Western blot showing knockdown of NEMO using siRNA in LNCaP cells. (G) NF-κB luciferase activity in LNCaP cells co-transfecting siRNAs against DRAIC and NEMO. (H) NF-κB luciferase reporter activity upon overexpression of constitutively active IKKβ (S177E/S181E) in LNCaP cells with transient overexpression of empty vector (EV) or a plasmid expressing full-length DRAIC (FL). Results expressed as mean ± s.d, n = 3, **P<0.01, *P<0.05.