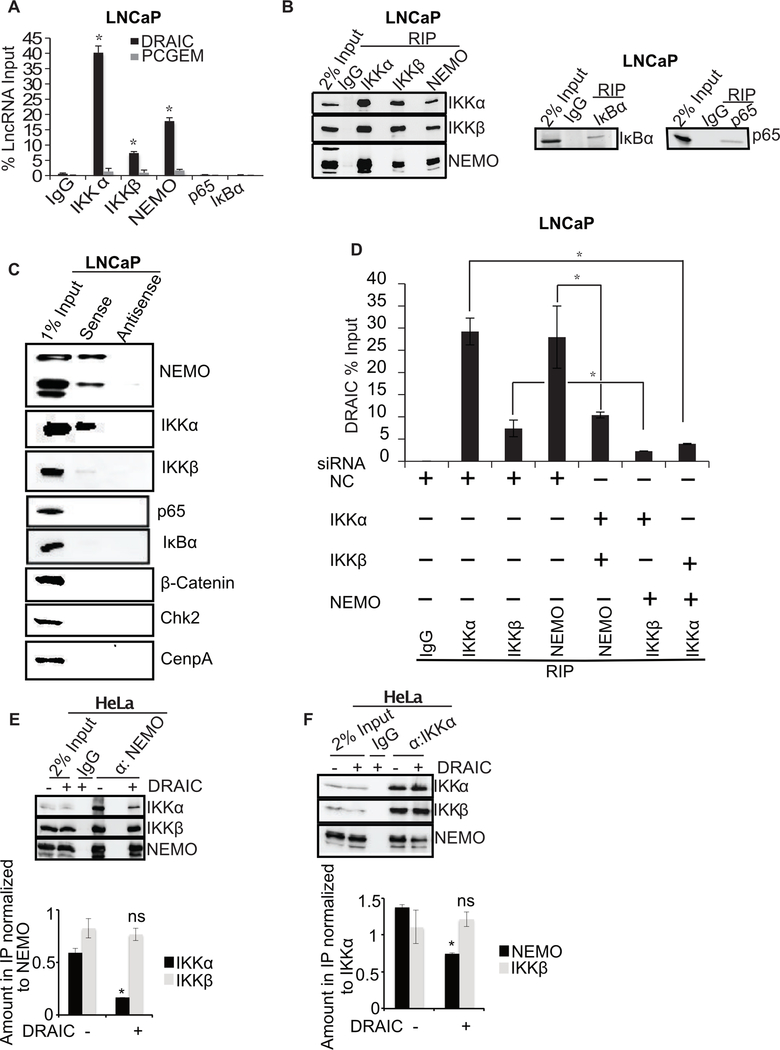
Figure 6. DRAIC interacts with IKK complex.
(A) RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay from LNCaP using NF-κB pathway proteins with antibodies against IKKα, IKKβ, NEMO, p65 and IκBα. RT-qPCR for DRAIC and PCGEM (a prostate tissue specific androgen regulated gene) expressed as % of input lncRNA in precipitates. (B) The immunoprecipitated samples in RIP were immunoblotted to ensure pull down of indicated proteins. (C) In vitro transcribed BrU labeled DRAIC sense (S) and antisense (AS) RNA was incubated in LNCaP cell lysates and pulled down with anti-BrdU antibody. The precipitate was immunoblotted for indicated proteins. (D) LNCaP cells after knockdown of two subunits of the IKK complex (Supplementary Fig. S3G–J). RIP assay performed with the remaining subunit followed by q-PCR for DRAIC. (E, F) NEMO (E) or IKKα (F) was immunoprecipitated from HeLa cells in presence and absence of stably overexpressed DRAIC and immunoblotted for indicated proteins. The amount of IKKα or IKKβ associated with NEMO (E) and the amount of NEMO or IKKβ associated with IKKα (F) were quantitated and plotted below the immunoblots. Mean±s.d, n=3, *p<0.05.