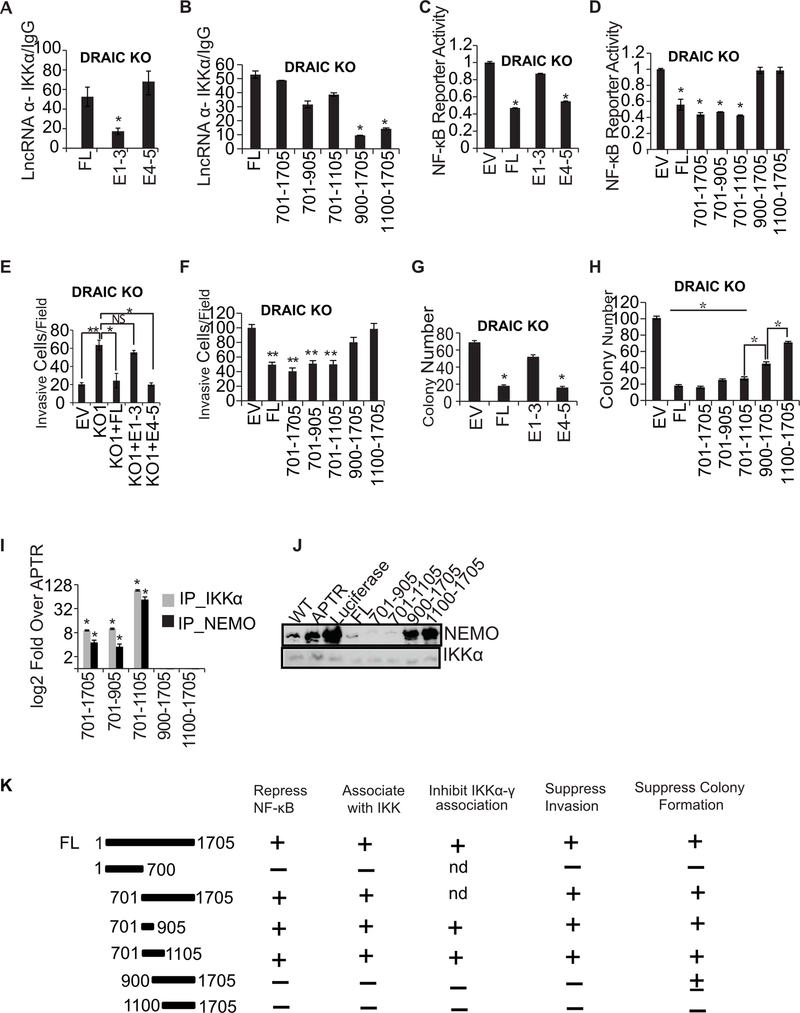
Figure 7. 701–905 bases of E4–5 associate with IKK and suppress invasion and NF-κB activity.
(A, B) RIP assay with IKKα in DRAIC KO cells after overexpressing DRAIC RNA and deletion constructs. RT-qPCR of DRAIC expressed as fold over signal from IgG IP. For A-H: Results expressed as mean ± s.d, n = 3, *P<0.05. (C, D) NF-κB luciferase reporter activity after expressing DRAIC or derivatives in DRAIC KO cells, normalized to activity in cells transfected with empty vector (EV). Mean ± s.d, n = 3, *P<0.05. (E, F) Invasion assay with DRAIC KO cells stably overexpressing DRAIC and derivatives. EV: empty vector. The number of invasive cells was quantified by taking 10 random microscopic fields. Mean± s.d, n = 3, **P<0.01, *P<0.05. (G, H) Soft-agar colony formation with DRAIC KO cells expressing DRAIC or derivatives. Mean ± s.d, n = 3, *P<0.05. (I) In vitro association of DRAIC or its derivatives with bacterially produced recombinant His-IKKα or GST-NEMO. RT-qPCR signal of DRAIC in the protein pull-downs normalized to the signal for APTR lncRNA (negative control). Mean±s.d, n=3, *p<0.05. (J) In vitro complex formation between recombinant NEMO and His6-IKKα in the presence of in vitro transcribed RNA indicated at top. His6-IKKα was immobilized on Nickel agarose beads and incubated with RNA followed by incubation with recombinant NEMO protein. The beads were then washed and boiled with Laemmli buffer and immunoblotted for the indicated proteins. WT: No RNA added. APTR and Luciferase were used as negative control RNA. (K) Summary of the results of the structure-function studies of DRAIC in prostate cancer cells. Nd: not done.