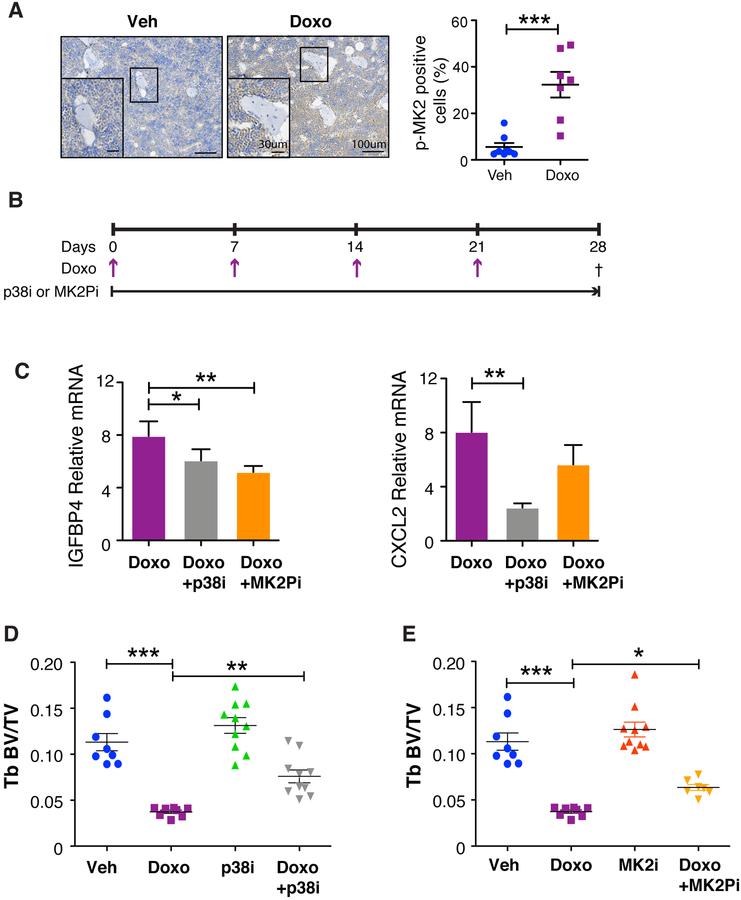
Figure 7: Inhibition of the p38MAPK-MK2 pathway limits SASP production and rescues chemotherapy-induced bone loss.
(A) Mice were sacrificed on day 28 and bone sections from vehicle and chemotherapy treated mice were stained for phosphor-MK2 and shows activation of the p38MAPK pathway following chemotherapy treatment. N≥7 per group. Data are presented as mean±SEM. (B) 16-week old C57BL/6 mice were treated with 4 once-weekly doses of vehicle (Veh) or doxorubicin (Doxo; 5 mg/kg) and provided ad libitum chow compounded with CDD-111 (p38i) or CDD-450 (MK2Pi). (C) Mice were sacrificed on day 28 and bone resident cells were isolated from tibias and the SASP factors IGFBB4 and CXCL12 were measured by qRT-PCR. qRT-PCR data are presented as mean±SD. (D-E) Femurs were isolated from animals treated with vehicle (Veh) or doxorubicin (Doxo) +/− p38i or +/− MK2Pi and measured by μCT to ascertain bone volume (BV) to trabecular (Tb) volume (BV/TV) of the p38i treatment cohort (D). Tb BV/TV of the MK2Pi treatment cohort (E). N≥8 per group. All data are presented as mean±SEM. *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001.