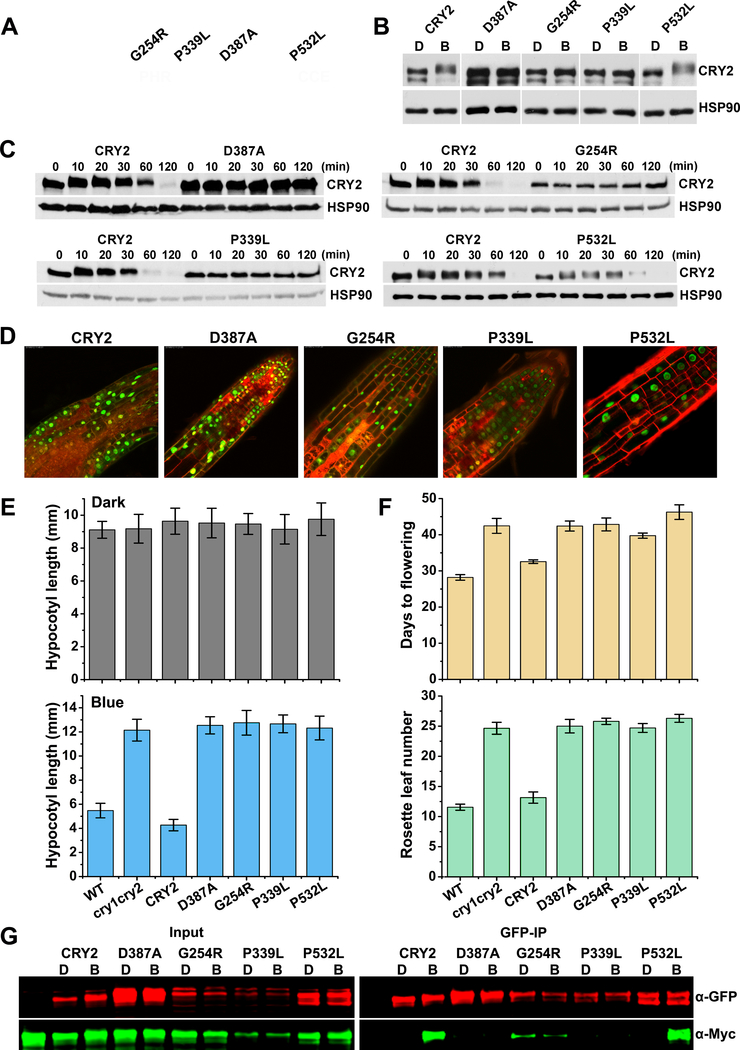
Figure 3. Photooligomerization is necessary but not sufficient for CRY2 function.
(A) Distribution of mutations found in Arabidopsis CRY2 genes. CRY2 is composed of PHR domain (1–489 aa) and the C-terminal extension (CCE, 490–612 aa) as indicated. cry2 mutants were roughly labelled on the top. G254R, the residue glycine at position 254 was changed to arginine; P339L, the residue proline at position 339 was changed to leucine; D387A, the residue aspartic acid at position 387 was changed to alanine; P532L, the residue proline at position 532 was changed to leucine. Green rectangle stands for nuclei localization signals.
(B) Phosphorylation analyses of cry2 mutants. GFP tag was fused to N-terminal of CRY2 and cry2 mutants to generate GFP-CRY2 and GFP-cry2 mutants, and the constructs were transformed into cry1cry2 double mutant background. Six-day-old dark-grown transgenic seedlings were transferred to 50 μmolm−2s−1 blue light for 20 min. Proteins were extracted, fractioned by SDS-PAGE gels, blotted and probed with anti-CRY2 antibody. Membranes were stripped and reprobed with anti-HSP90 for loading controls. The arrowhead indicates the electrophoretic-mobility-shift (phosphorylated) CRY2 and the arrow indicates mostly the unphosphorylated CRY2.
(C) Degradation analyses of cry2 mutant proteins. Six-day-old dark-grown transgenic seedlings were transferred to 50 μmolm−2s−1 blue light for the indicated time (10, 20, 30, 60,120 min). Proteins were extracted, fractioned by SDS-PAGE gels, blotted and probed with anti-CRY2 antibody. Membranes were stripped and reprobed with anti-HSP90 for loading controls.
(D) Subcellular localization analyses of cry2 mutant proteins. Seven-day-old GFP-cry2 mutant seedlings grown in long day were analyzed by confocal microscope. PI stain (red color) was used to show the cell boundaries. Scale bar: 20 μm.
(E) Measurement of hypocotyl length of transgenic cry2 mutants. Seedlings were grown in the dark (upper pannel) or continuous blue (10 μmolm−2s−1, lower pannel) for six days before measurement. Hypocotyl lengths with standard deviations (n≥20) are shown.
(F) Measurement of flowering time of transgenic cry2 mutants. Plants were grown in long day (16 hour light / 8 hour dark) condition. Days to flowering (upper pannel) and rosette leaf numbers (lower pannel) with standard deviations are shown (n≥20).
(G) Photooligomerization analyses of cry2 mutants. Seven days old transgenic Arabidopsis seedlings co-expressing GFP-CRY2 and Myc-CRY2 or GFP-cry2 mutants and Myc-cry2 mutants were grown in the dark, exposed to blue light of 30 μmolm−2s−1 for 5 min or left in the dark. GFP tagged proteins were co-immunoprecipitated by GFP-trap beads. The immunoblots were analyzed by probing with anti-GFP and anti-Myc antibodies.