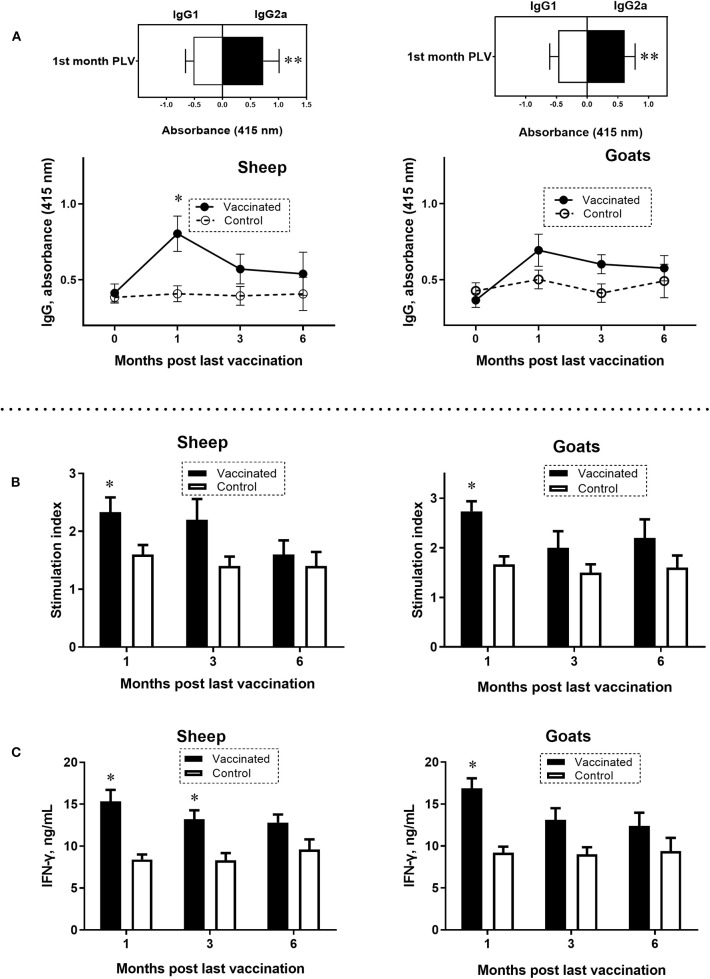
Figure 2.
Antigen-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) IgG, IgG1, and IgG2a antibody responses (A) and lymphocyte stimulation index (B) and interferon γ (IFN-γ) production (C) in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of sheep and goats at 0 or first, third, and sixth month PLV. A mixture of Brucella L7/L12, Omp16, Omp19, and superoxide dismutase proteins was used to simulate PBMCs and in ELISA. Sheep and goats were vaccinated thrice concurrently via the subcutaneous and conjunctival route. Animals in the control group received only the adjuvant in phosphate-buffered saline. Statistical analysis was performed using two-way analysis of variance followed by Sidak's multiple-comparisons test. ELISA antibody levels were presented as OD ± standard error. Cell proliferation results were converted to stimulation index [counts per minute (cpm) of wells containing antigens/cpm in the absence of antigens] for comparison. Antigen-specific IFN-γ production was determined for each individual animal by subtracting the background concentration of IFN-γ in wells without antigen from the IFN-γ concentration in wells with antigen. *P = 0.0007 vaccine group vs. control; **P = 0.014–0.02 IgG2a vs. IgG1 at the first month PLV. Data of lymphocyte stimulation index and levels of IFN-γ are presented as mean ± standard error; *P = 0.047–P < 0.0001 vaccine vs. control group.