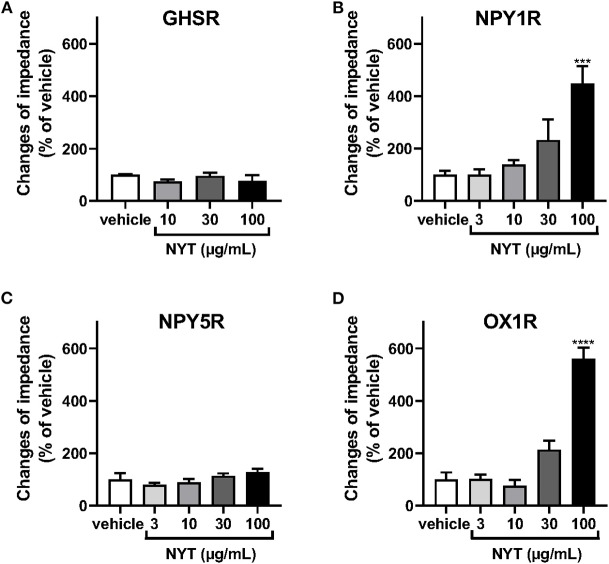
Figure 1.
Effects of Ninjinyoeito (NYT) on impedance changes in cells expressing several G-protein-coupled receptors, which activate hyperphagia signaling in the central nervous system using the CellKey™ assay. The cells stably expressing growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1a (GHSR) (A, n = 6–8), neuropeptide Y1 receptor (NPY1R) (B, n = 6), neuropeptide Y5 receptor (NPY5R) (C, n = 6), or orexin 1 receptor (OX1R) (D, n = 6) were treated with NYT (3–100 μg/kg) or its vehicle (control). The rate of change in impedance was measured using the CellKey™ system and expressed as the difference of the minimum impedance and maximum impedance after drug injection. The data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. *** and **** indicate p < 0.001 and p < 0.0001, respectively, compared with the control; Bonferroni's multiple comparison test following one-way ANOVA.