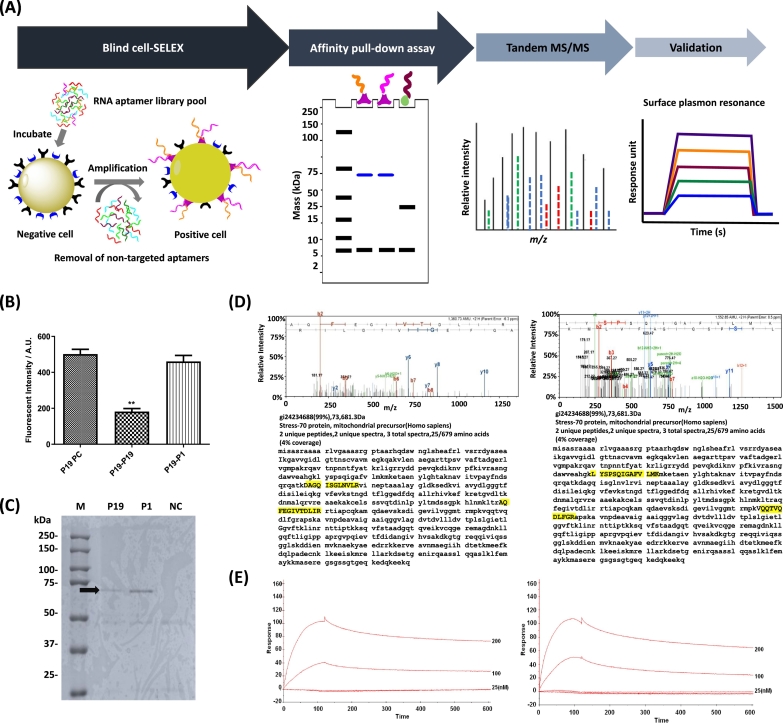
Figure 6.
Blind SELEX to identify potential biomarkers on pancreatic cancer. (A) The schematic workflow of blind SELEX is depicted. After untargeted SELEX to identify differently expressed markers on plasma membrane of PANC-1 cells, aptamers are enriched in vitro. Target ligands were retrieved via affinity pull-down assays using biotinylated aptamers. After affinity pull-down assays, MS/MS is used to achieve peptide fingerprinting. Finally, the binding of aptamer with the target ligand is validated by surface plasmon resonance. (B) Competition assay was performed to determine whether P19 and P1 bind to the same epitope. The fluorescence intensity was quantified using confocal microscopy. *One-way ANOVA test; *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01. (C) Ten percent of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis was used to separate immobilized protein samples after pull-down with biotinylated P19, P1, and negative control RNAs. Coomassie-stained gels: M (marker), P19 (lane 1), P1 (lane 2), and NC (irrelevant RNA, lane 3). Arrow indicates target antigens. (D) MS/MS spectra of aptamer binding ligand. Peptide matching and MS/MS spectra of P19 (left) and P1 (right) affinity-purified peptides. Inset: amino acid sequence of the parent peptide showing b- and y-ion series coverage. Target epitopes are highlighted in yellow. (E) Biosensor analysis of the mortalin-aptamer interaction. Binding of mortalin to the P19 (left) and P1 (right) was shown. Biotinylated P19 or P1 was bound to a streptavidin-coupled carboxyl methyl dextran surface, and binding was measured using the SPR technique. The increased response unit was shown in a dose-dependent manner.