Fig. 3.
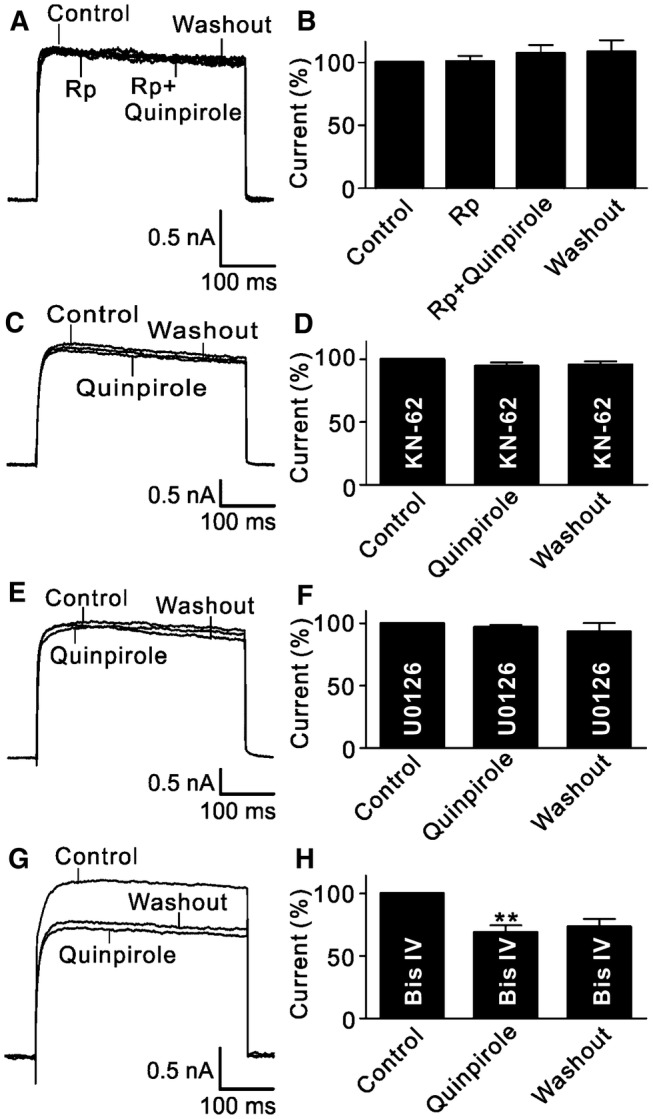
Signaling pathways involved in the quinpirole-induced suppression of outward K+ channels. A Representative current traces recorded from an RGC, showing that quinpirole did not change the outward K+ current amplitude when the cell was perfused with Rp-cAMP (2 μmol/L). B Bar chart summarizing the changes in K+ current amplitudes at +30 mV under different conditions (n = 13). C, D Sample current traces showing that the CaMKII signaling inhibitor KN-62 (10 μmol/L) blocked the quinpirole-induced suppression of outward K+ currents (C), and summary data are shown in (D) (n = 11). E Sample current traces showing that U0126 (10 μmol/L), a MAPK/ERK signaling inhibitor, blocked the quinpirole-induced suppression of outward K+ currents. F Bar chart summarizing the changes of outward K+ current amplitudes at +30 mV (n = 12). G Representative current traces recorded from an RGC, showing that the PKC inhibitor Bis IV (10 μmol/L) failed to block the quinpirole-induced suppression of outward K+ currents. H Summary bar graphs for the effect of Bis IV on the quinpirole-induced suppression of outward K+ currents (n = 14, **P <0.01 vs control).
