Figure 1.
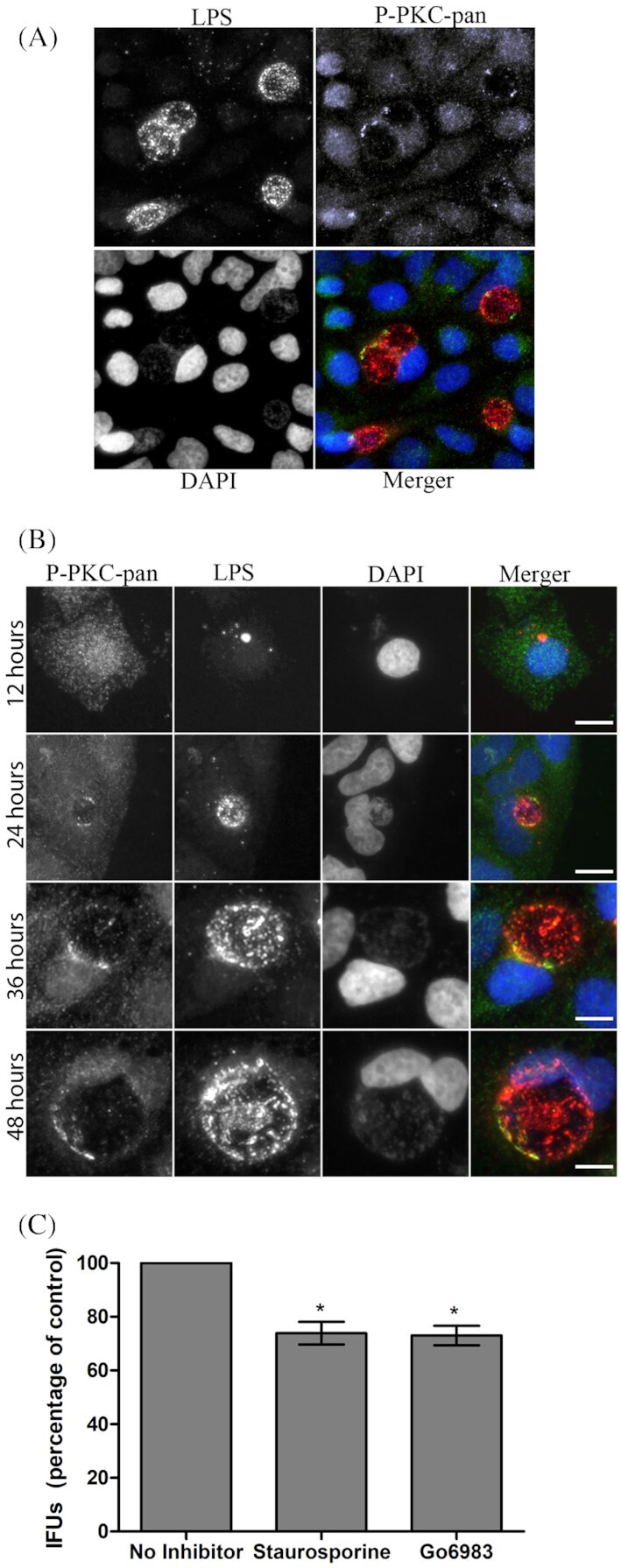
PKC is recruited to the chlamydial inclusion and PKC inhibitors reduce C. trachomatis IFUs. (A) HeLa cells were infected with C. trachomatis for 36 hours and prepared for immunofluorescence microscopy. Phospho-PKC-pan antibody was used to detect endogenous levels of phosphorylated PKCs recruited to the chlamydial inclusion. (B) Phospho-PKC-pan recruitment was monitored over a time course of infection. Shown are 12, 24, 36 and 48 hours post-infection. (C) HeLa cells were infected with C. trachomatis L2 and treated with staurosporine (0.5 µM) or Go6893 (0.5 µM) with the inhibitors being present throughout infection. At 48 hours post-infection, the cells were lyzed to release Chlamydia and cell lysates were serially diluted and used to infect HeLa cell monolayers. Infection was allowed to proceed for 18 hours, cells were fixed with cold methanol, processed for microscopy and 30 fields of view were counted for each condition in triplicate. Error bars indicated standard deviation. Scale bar, 10 µm. *P < 0.001.
