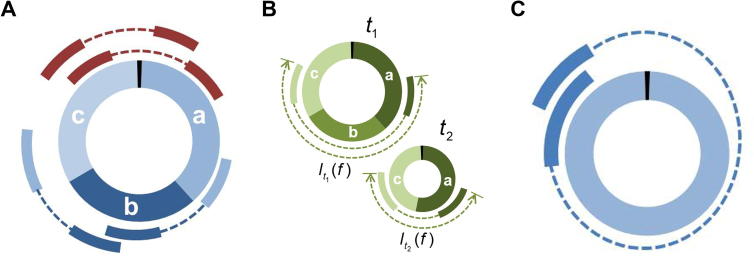
Supplementary Figure S1.
Schematics of read mapping and fragment length in circRNAs A. CircAST uses the fragments located not only between the junction sites (blue) but also across the junction (red) in circular transcript assembly and quantification. B. Alignments of reads to the genome may be consistent with multiple circular transcripts. The implied length of the fragment f, denoted as lt(f), may be different because of the prevalence of AS in circular transcripts. The circular transcripts t1 and t1 differ by an internal exon b, with the implied length lt1(f) > lt2(f). C. If the length of a circRNA is shorter than the fragment length, the two reads from the fragment termini could possibly be aligned to the same region in circRNA. a, b, c represent 3 different exons and the site colored in black represents a BSJ.