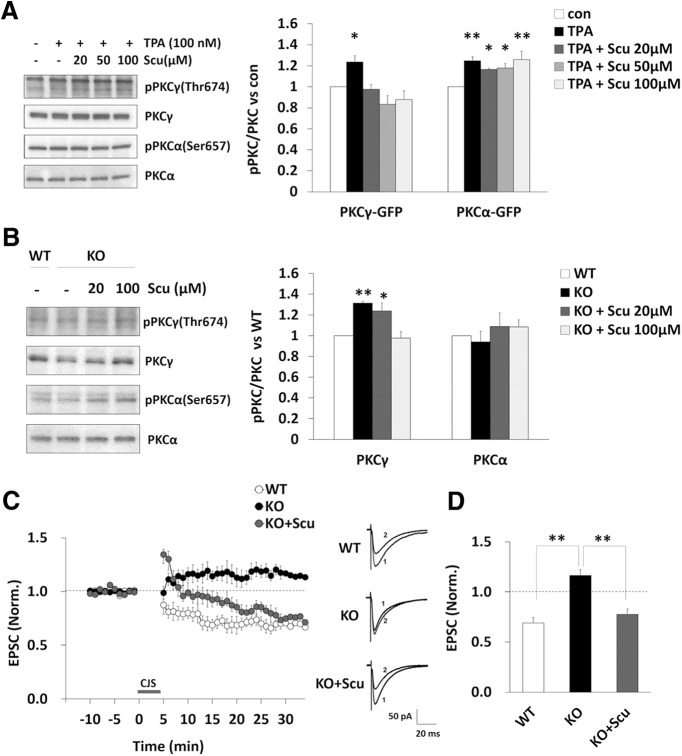
Figure 7.
Rescue of impaired LTD in DGKγ KO mice by a PKCγ inhibitor. A, COS-7 cells overexpressing PKCγ-GFP or PKCα-GFP were cultured for 48 h. The cells were treated with TPA (100 nm) for 30 min after preincubation with or without scutellarin (Scu; 20, 50, or 100 μm) for 30 min. The lysates from the cells were subjected to Western blotting and probed with anti-phospho-PKCγ, anti-PKCγ, anti-phospho-PKCα, and anti-PKCα antibodies. Quantification of the autophosphorylation of PKCγ and PKCα was performed by ImageJ. The phosphorylation levels of PKCγ and PKCα were normalized to the PKCγ and PKCα expression levels. The ratio of the phosphorylation of PKCγ and PKCα to that in the control was plotted (PKCγ-GFP: n = 6; PKCα-GFP: n = 6); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (vs control), followed by Dunnett’s test. B, Acute cerebellar slices from WT and DGKγ KO mice were incubated with or without Scu (20 or 100 μm) for 1 h. Lysates from the slices were subjected to Western blotting as described in A (PKCγ: n = 3; PKCα: n = 3); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (vs WT), followed by Dunnett’s test. C, Changes in the PF-EPSC amplitude before and after the CJS of PF (1 Hz, 300 s) with depolarization applied at time 0. A PKCγ inhibitor Scu (100 μm) was added to the extracellular solution prior to stimulation. The PF-EPSC amplitude was normalized to the mean over 10 min before CJS (WT: n = 8; KO: n = 8; KO+Scu: n = 7). Sample traces immediately before (1) and 30 min after (2) CJS. D, Average PF-EPSC amplitude over the 21- to 30-min period after CJS; **p < 0.01, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM.