Fig. (3).
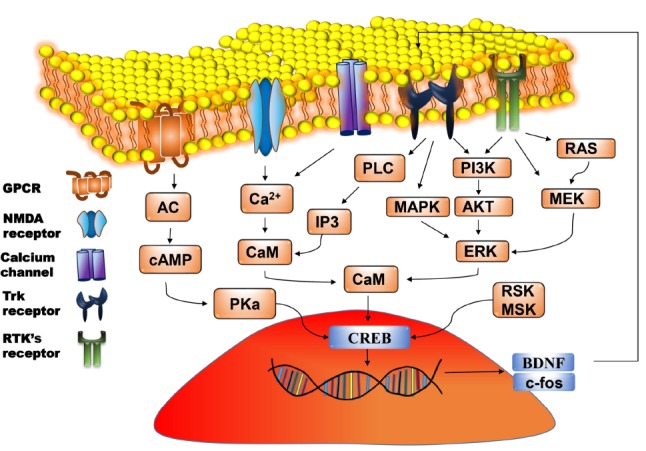
Molecular pathway of CREB-BDNF activation. Signals due to various stimuli arrive at the cell membrane and activates the corresponding receptors. This results in the activation of downstream signalling cascades and generation of second messengers which activates protein kinase. PKA translocates to the nucleus and causes phosphorylation of CREB, which then binds with the CRE region resulting in the transcription of genes such as BDNF and c-fos. BDNF binds with TrkB receptors and further enhances the phosphorylation of CREB. AC: Adenyl cyclase; AKT: Protein kinase B BDNF: Brain derived neurotrophic factor; CAM: Calmodulin; cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CREB: cAMP response element binding protein; ERK: Extracellular signal regulated kinase; GPCR: G protein coupled receptor; IP3: Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate; MAPK: Mitogen activated protein kinase; MEK: Mitogen activated protein kinase; MSK: Mitogen and stress activated protein kinase; NMDA: N-methyl d-aspartate receptors; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinases; PKa: PLC: Phospholipase C; RTK’s: Receptor tyrosine kinase and TrkB: Tropomyosin receptor kinase/ tyrosine receptor kinases ; RSK: 90 kDa Ribosomal S6 kinase. (A higher resolution / colour version of this figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).
