Fig. 2.
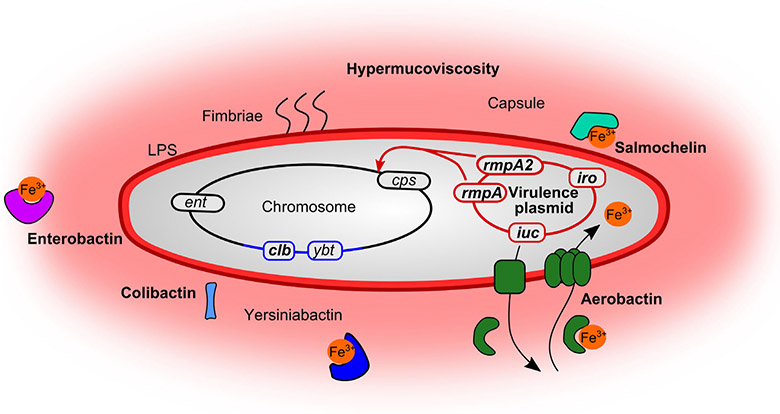
Defining features of hvKp. Defining features (in bold) of hvKp include both chromosomal and plasmid-encoded features that result in the enhanced virulence of hvKp. These are in addition to factors that contribute to the pathogenesis of all K. pneumoniae (not in bold): the siderophore systems enterobactin (ent) and yersiniabactin (ybt), as well as the fimbriae and LPS on the surface. Many hvKp encode yersiniabactin, as well as the secreted toxin colibactin (clb) within an integrative and conjugative element in the chromosome, shown in blue. Plasmid-encoded transcriptional regulators rmpA/rmpA2 (regulator of mucoid phenotype) regulate the chromosomal capsule (cps) loci causing hypercapsule associated with the hypermucoviscous phenotype of hvKp. hvKp strains are frequently of the K1 and K2 capsule types. Encoded on virulence plasmids are also the salmochelin (iro) and aerobactin (iuc) siderophore systems. The details of aerobactin export, binding to iron, and import for iron acquisition are representative of all the siderophores, as each system is typically complete for biosynthesis, export and import of the respective siderophore
