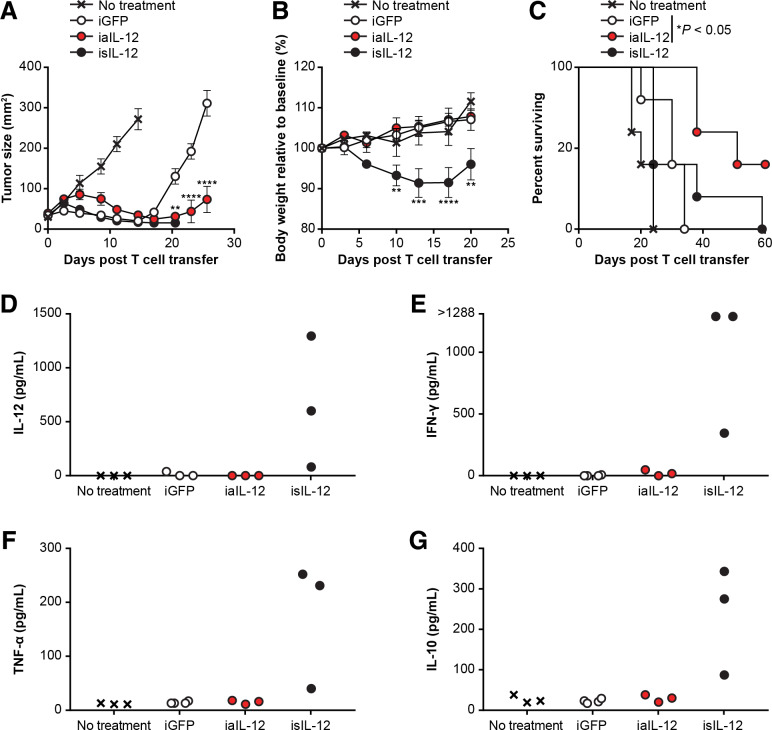
Figure 5.
iaIL-12 enhanced the efficacy of tumor-specific T-cell therapy without evidence of toxicity. Mice with established B16-OVA tumors were treated with 15×106 OT-I cells that were transduced with the vectors indicated. isIL-12 served as a positive control for systemic IL-12 exposure. All mice received 550-cGy whole-body radiation before cell infusion. N=5 mice per group. (A) Tumor area was determined by serial measurements at the time points indicated on the x-axis. Error bars represent thestandard error of the mean. P values represent comparisons between iGFP and iaIL-12 at each time point using a two-way ANOVA multiple comparisons test. **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001. (B) The change in body weight relative to baseline is shown. Error bars show the standard error of the mean. P values represent comparisons between iGFP and isIL-12 at each time point using a two-way ANOVA multiple-comparisons test. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001. (C) The survival of tumor-bearing mice that received cell transfer was determined as shown. Survival was greater for iaIL-12 than iGFP (p=0.026 by Mantel-Cox test). (D–G) Serum cytokine levels were determined on day 14 after treatment. The cytokines were measured with a multiplex cytokine kit. Values for individual mice are plotted. The cytokine for each analyte is indicated on the y-axis. isIL-12 serves as a positive control. ANOVA, analysis of variance; iaIL-12, inducible anchored interleukin-12; iGFP, inducible green fluorescent protein; isIL-12, inducible secreted interleukin-12; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.