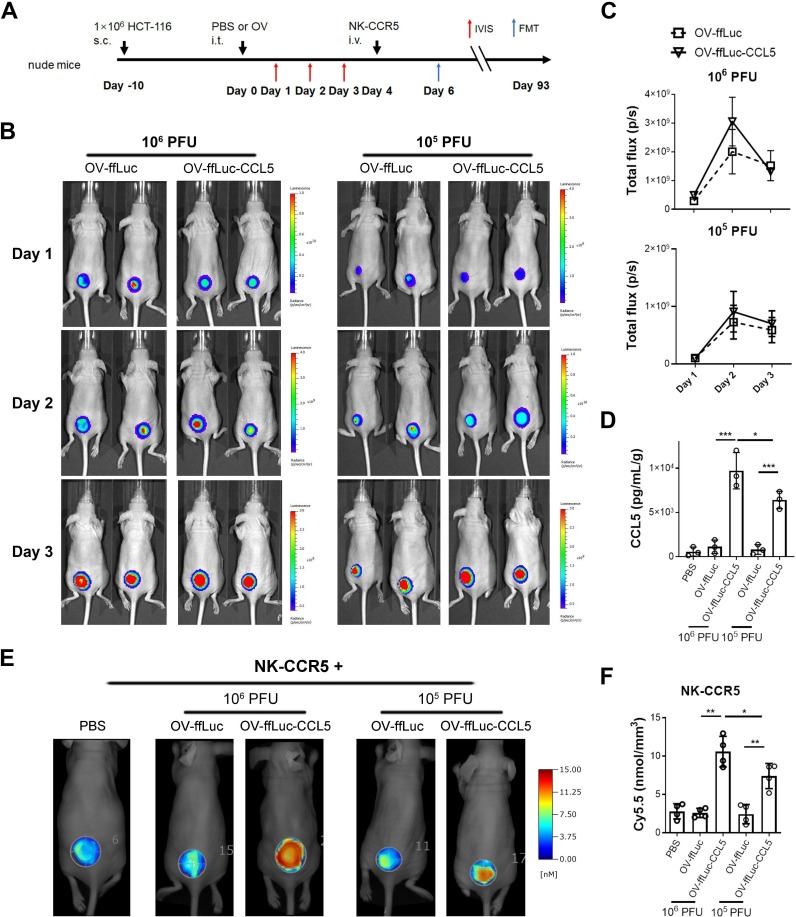
Figure 6.
CCL5-expressing vaccinia virus enhances NK cell infiltration. (A) Schematic description of animal experiments. Ten days after HCT-116 cell inoculation, 106 or 105 PFU of oncolytic virus were injected intratumorally. The viral replications were monitored for 3 days by IVIS imaging. Next, 5×106 NK-CCR5 cells were injected 4 days after virus injection. The accumulation of NK-CCR5 cells was examines by FMT assay. (B, C) Vaccinia virus expansion was not affected by CCL5 transgene in vivo (n=5). (D) Four days after virus treatment, tumors were isolated and homogenized (n=3). CCL5 concentrations were determined using ELISA. (E, F) NK cells labelled with Cy5.5 dye were injected into mice pretreated with PBS or indicated virus (n=4), after 48 hours, the tumorous infiltration of NK cells was determined. Data are presented as the means±SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005. FMT, fluorescence molecular tomographic; IVIS, in vivo imaging system; i.t., intratumorous; i.v., intravenous; NK, natural killer; PFU, plaque-forming unit; S.C., subcutaneous; OV, oncolytic viruse; PBS, phosphate buffered saline.