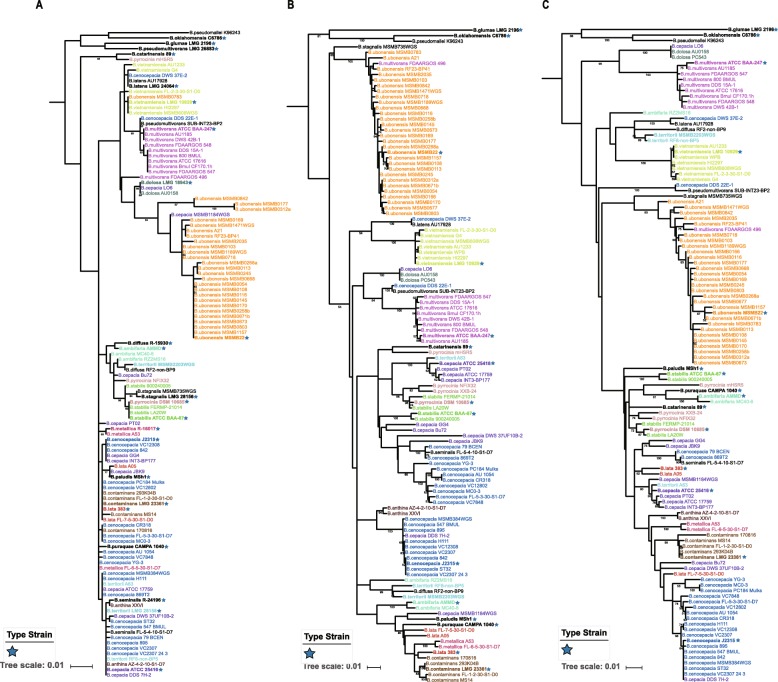
Fig. 1.
The phylogenetic relationships of BCC strains based on (A) 16S rRNA, (B) recA and (C) hisA sequences.The maximum-likelihood trees were constructed from the alignments of (a) full length 16S rRNA (1539 bp), (b) full length recA (1071 bp) and (c) full length hisA (756 bp) sequences. B. pseudomallei K96243, B. oklahomensis C6786T and B. glumae LMG 2196T were chosen as outgroups. Numbers below branches are bootstrap support values from 1000 replicates if equal to or larger than 50%. Type strains are printed in bold font as well as marked by a blue star (B. ubonensis MSMB22 is the representative genome of this species; because of its examined high-quality and unavailability of the whole genome of this species, we treated MSMB22 as the same as the type strain of B. ubonensis in this paper). Species with at least two members are colored except B. pseudomultivorans, B. latens, B. diffusa, B. stagnalis and B. seminalis in (a); species with single members (and outgroups) are black